NAPs and TIVA and pEEG monitoring
Quick summary 🧵 for amongst others
@JulianCorbettF
NAP5
Awareness
-TIVA was associated with a doubling in frequency of accidental awareness (during general anaesthesia (AAGA)
-what a lot of people missed was that when TIVA was used correctly in a TCI mode there was no signal
-most AAGA during TIVA was due to syringe/delivery errors, programming errors, erroneous use of manual infusions especially when converting from volatile to TIVA (eg to transfer sick pt to ICU or radiology)
-6% of GAs were TIVA. 90% of these in theatre were TCI. Outside theatre 18% were TCI.
rcoa.ac.uk
-pEEG (BIS) use was low at 2.8%
-much higher with TIVA:
*8% without NMB
*23% with NMB
-report recommended universal use of BIS when TIVA used with paralysis
rcoa.ac.uk
1/5
Quick summary 🧵 for amongst others
@JulianCorbettF
NAP5
Awareness
-TIVA was associated with a doubling in frequency of accidental awareness (during general anaesthesia (AAGA)
-what a lot of people missed was that when TIVA was used correctly in a TCI mode there was no signal
-most AAGA during TIVA was due to syringe/delivery errors, programming errors, erroneous use of manual infusions especially when converting from volatile to TIVA (eg to transfer sick pt to ICU or radiology)
-6% of GAs were TIVA. 90% of these in theatre were TCI. Outside theatre 18% were TCI.
rcoa.ac.uk
-pEEG (BIS) use was low at 2.8%
-much higher with TIVA:
*8% without NMB
*23% with NMB
-report recommended universal use of BIS when TIVA used with paralysis
rcoa.ac.uk
1/5
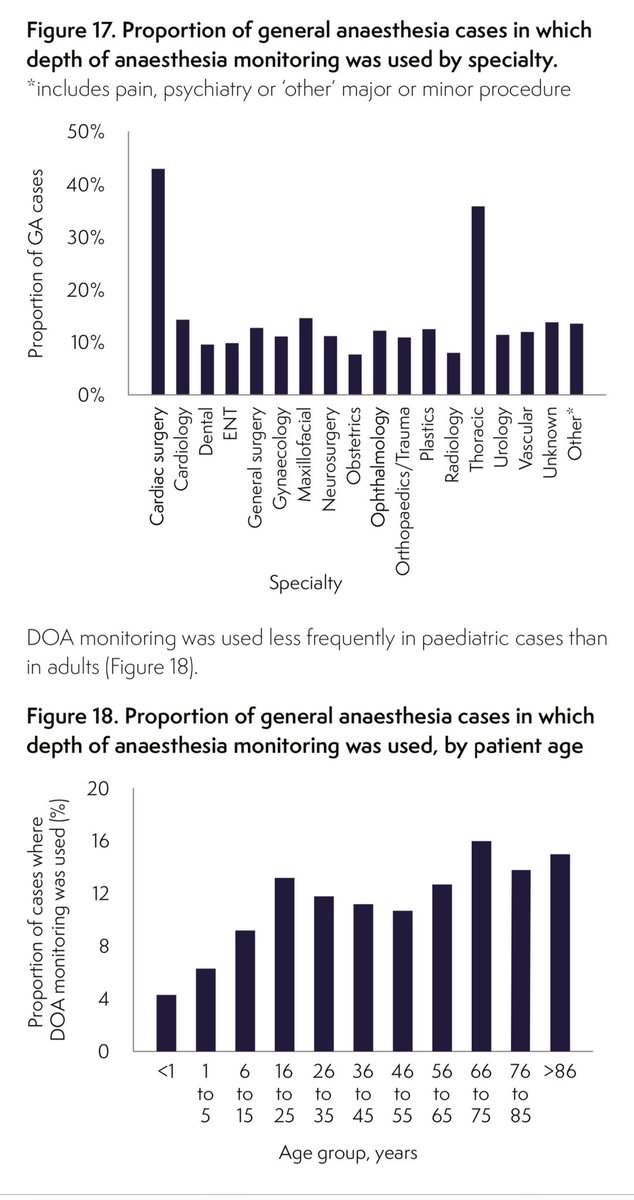
In NAP6 (anaphylaxis) we took stock of all drugs used during anaesthesia
-use of TIVA rose to 8%
-pEEG monitoring was used in 12%
*rising to 32% with TIVA
*38% with TIVA + NMB
-with variation by specialty, anaesthetist seniority & BMI
rcoa.ac.uk
2/5
-use of TIVA rose to 8%
-pEEG monitoring was used in 12%
*rising to 32% with TIVA
*38% with TIVA + NMB
-with variation by specialty, anaesthetist seniority & BMI
rcoa.ac.uk
2/5
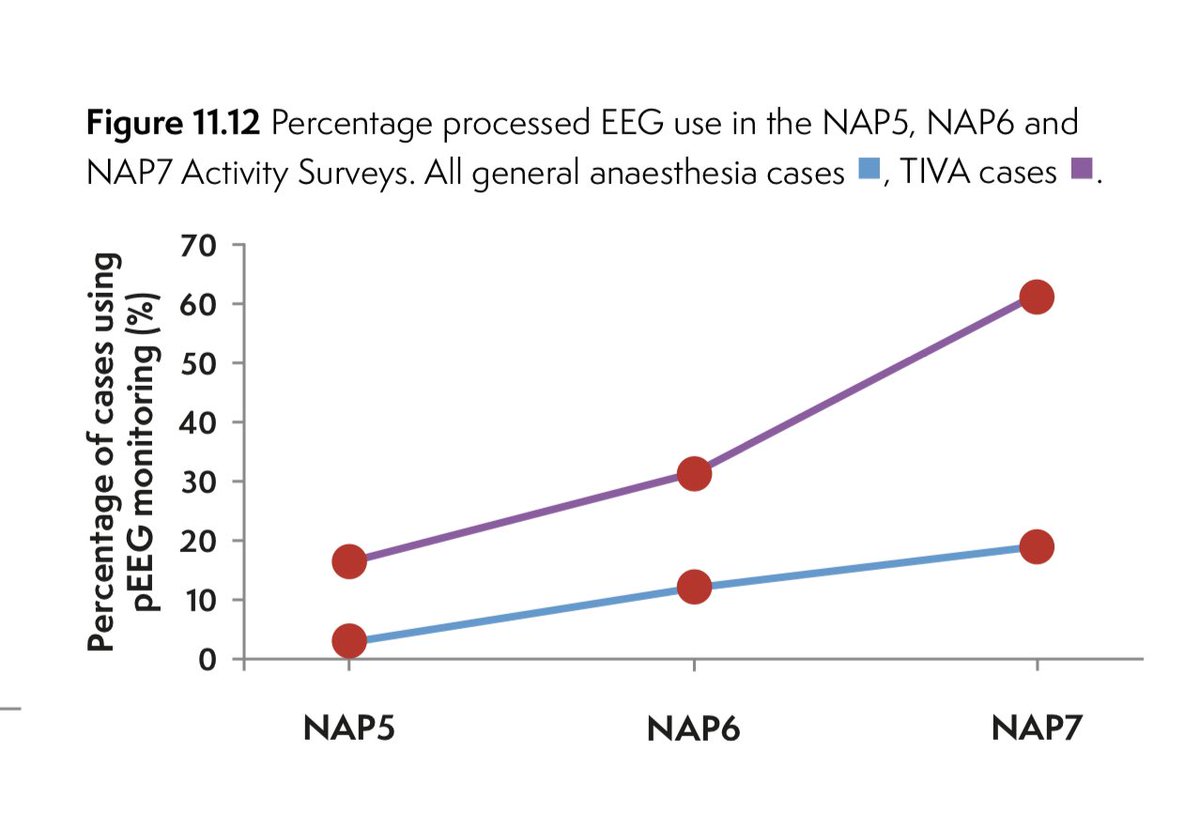
In NAP7 (perioperative cardiac arrest) we collected data on TIVA & pEEG use but not on NMB use
-TIVA use rose dramatically to 26%
*a 4-fold rise in a decade
-pEEG rose to 19%
*a 7-fold rise
-pEEG use during TIVA rose to 62% (likely close to 100% during TIVA + NMB though we did not measure this)
-implying good impact of the previous recommendation (which has been repeated by others)
rcoa.ac.uk
3/5
-TIVA use rose dramatically to 26%
*a 4-fold rise in a decade
-pEEG rose to 19%
*a 7-fold rise
-pEEG use during TIVA rose to 62% (likely close to 100% during TIVA + NMB though we did not measure this)
-implying good impact of the previous recommendation (which has been repeated by others)
rcoa.ac.uk
3/5
In the registry phase of NAP7 a common theme was of isolated severe hypotension or leading to perioperative cardiac arrest.
This related to patients who were high risk from
-old age
-frailty
-high ASA
-acute disease processes
Within this cohort both propofol & TIVA with propofol
& remifentanil (causing bradycardia) were prominent leading the authors to
-highlight it
-recommend careful & cautious drug titration
-recommend increased monitoring
-recommend consideration of other drugs
The issue is discussed in this chapter
rcoa.ac.uk
4/5
This related to patients who were high risk from
-old age
-frailty
-high ASA
-acute disease processes
Within this cohort both propofol & TIVA with propofol
& remifentanil (causing bradycardia) were prominent leading the authors to
-highlight it
-recommend careful & cautious drug titration
-recommend increased monitoring
-recommend consideration of other drugs
The issue is discussed in this chapter
rcoa.ac.uk
4/5
NAPs and TIVA
Conclusions
-well documented changes in practice over the last decade
-marked increase in use
-a risk for AAGA , especially if used without care or attention to detail
-pEEG monitoring goes hand in hand and has increased dramatically
-TIVA (especially prop+remi) also a risk factor in high risk cases for hypotension or bradycardia induced perioperative cardiac arrest
5/5 END
Conclusions
-well documented changes in practice over the last decade
-marked increase in use
-a risk for AAGA , especially if used without care or attention to detail
-pEEG monitoring goes hand in hand and has increased dramatically
-TIVA (especially prop+remi) also a risk factor in high risk cases for hypotension or bradycardia induced perioperative cardiac arrest
5/5 END
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...