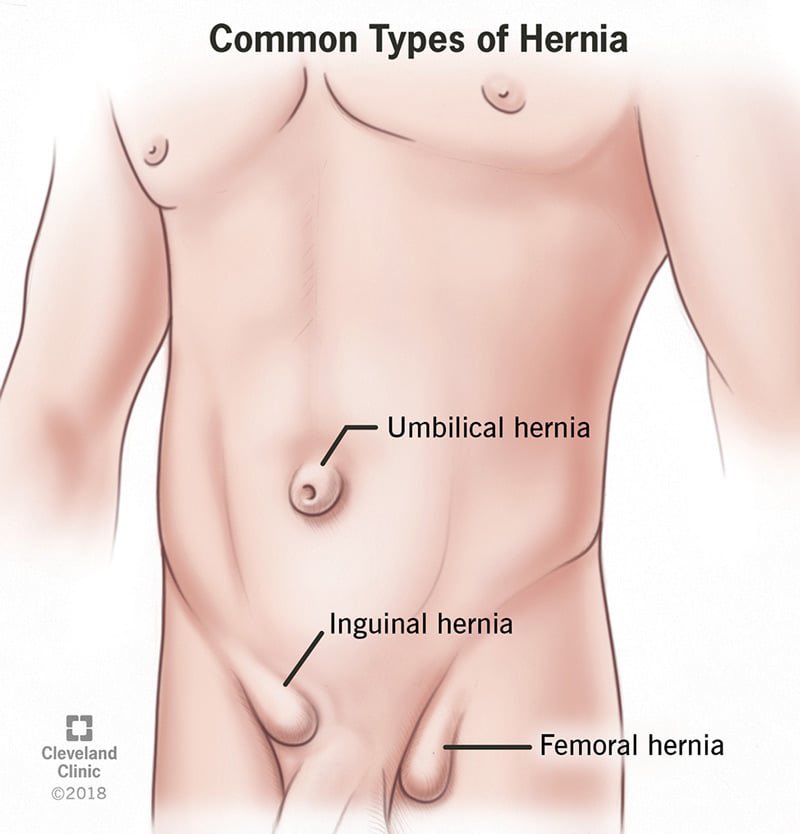
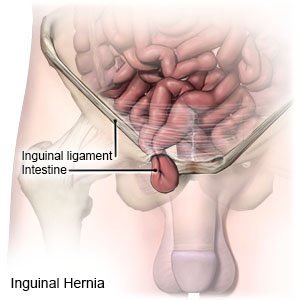
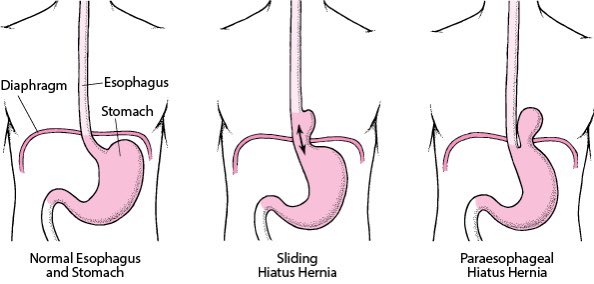
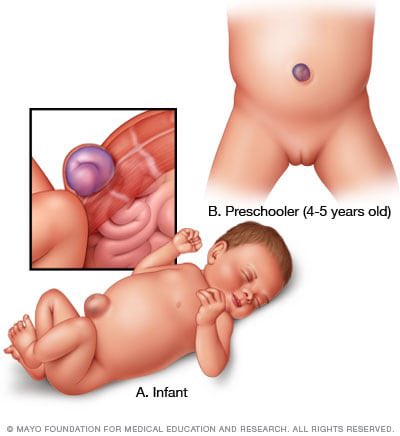
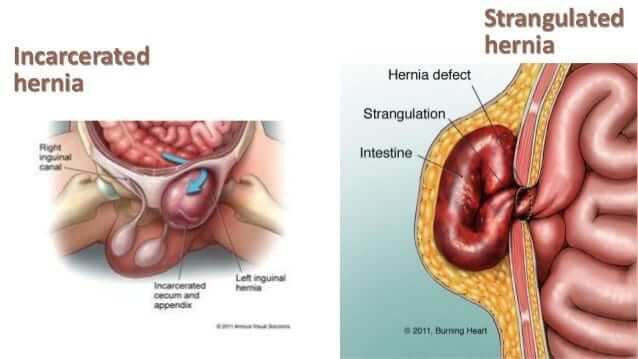
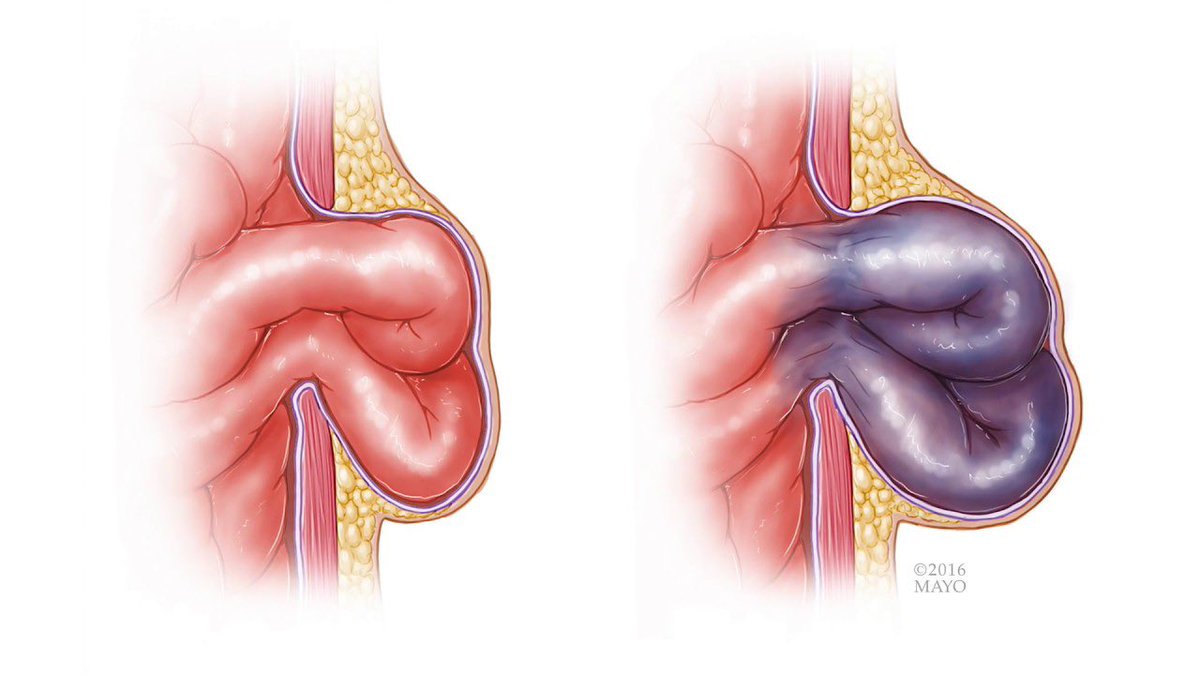
Hernia is a medical condition that occurs when an organ or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue.
It most commonly affects the abdominal wall, but can also occur in the groin, thigh, and upper torso.
It most commonly affects the abdominal wall, but can also occur in the groin, thigh, and upper torso.
Symptoms:
• Bulge or lump that may or may not be painful.
• Pain or discomfort in the affected area, especially when coughing or lifting heavy objects.
• Nausea, vomiting, or constipation in case of a strangulated hernia.
• Bulge or lump that may or may not be painful.
• Pain or discomfort in the affected area, especially when coughing or lifting heavy objects.
• Nausea, vomiting, or constipation in case of a strangulated hernia.
Risk Factors:
• Being overweight or obese.
• Chronic coughing or sneezing.
• Pregnancy or childbirth.
• Previous abdominal surgery.
• Family history of hernias.
• Chronic constipation or straining during bowel movements.
• Being overweight or obese.
• Chronic coughing or sneezing.
• Pregnancy or childbirth.
• Previous abdominal surgery.
• Family history of hernias.
• Chronic constipation or straining during bowel movements.
Diagnosis:
Your doctor can diagnose a hernia through a physical examination.
They may be able to feel the hernia by pressing on the affected area.
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scan may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Your doctor can diagnose a hernia through a physical examination.
They may be able to feel the hernia by pressing on the affected area.
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scan may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
The most common treatment for a hernia is surgery.
Surgery involves repairing the weakened muscle or tissue and repositioning the protruding organ.
The most common treatment for a hernia is surgery.
Surgery involves repairing the weakened muscle or tissue and repositioning the protruding organ.
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...