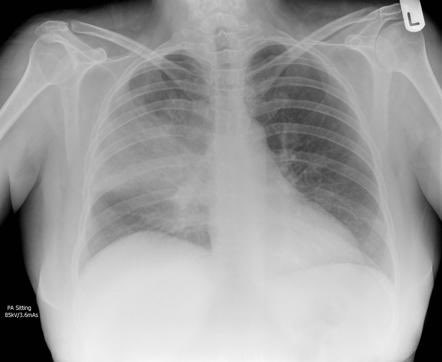
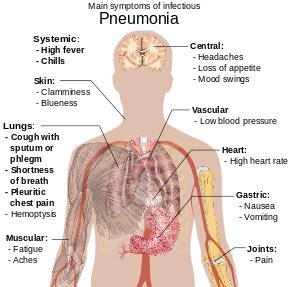
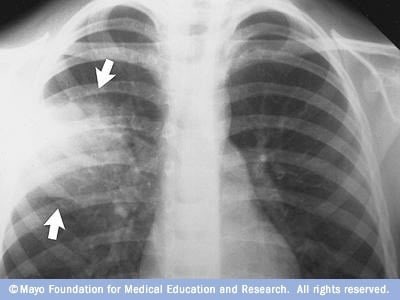
بتكلم عن اكثر موضوع متكرر بالاختبار وبالمستشفى
Pneumonia 📌
تقدر تجمع الثريد وتستخدمه للمراجعة
Pneumonia 📌
تقدر تجمع الثريد وتستخدمه للمراجعة
There are several different types of pneumonia, which can be classified based on the cause of the infection, the location of the infection in the lungs, or the type of pneumonia cells. Some of the most common types of pneumonia include:
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): This is the most common type of pneumonia and occurs in people who have not been recently hospitalized. It is caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses, and fungi and can be acquired in the community or in the home.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP): This type of pneumonia occurs in people who have been recently hospitalized, typically within 48-72 hours after being admitted to the hospital. It is caused by a variety of bacteria and can be more severe than community-acquired pneumonia.
Aspiration pneumonia: This type of pneumonia occurs when a person aspirates, or inhales, foreign material such as food, vomit, or saliva, into their lungs. It can occur in people with swallowing disorders, neurological conditions, or who are unconscious.
Risk factors for pneumonia include being over the age of 65, having a weakened immune system, chronic lung disease such as (COPD) or cystic fibrosis, and smoking. Other include having a recent upper respiratory infection, exposure to toxins or chemicals.
treatment options for pneumonia.
Antibiotics: Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics.
Common antibiotics used to treat pneumonia include penicillin, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones.
Antibiotics: Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics.
Common antibiotics used to treat pneumonia include penicillin, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones.
Antiviral medications: For viral pneumonia, The most common antiviral medications
are oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) for influenza and ribavirin for RSV. These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
are oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) for influenza and ribavirin for RSV. These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
Oxygen therapy: may be needed if the patient has low oxygen levels. This can be administered through a nasal cannula or a mask that covers the nose and mouth. The goal of oxygen therapy is to bring oxygen levels back to normal and prevent complications such as respiratory failure
Pneumonia can lead to several complications, including:
1 Respiratory failure: Difficulty breathing and oxygenation of blood
2 Septicemia: Blood infection
3 Pleural effusion: Fluid buildup in the pleural cavity
4 Empyema: Pus accumulation in the pleural cavity
5 Lung abscess
1 Respiratory failure: Difficulty breathing and oxygenation of blood
2 Septicemia: Blood infection
3 Pleural effusion: Fluid buildup in the pleural cavity
4 Empyema: Pus accumulation in the pleural cavity
5 Lung abscess
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...