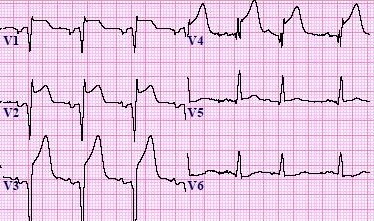
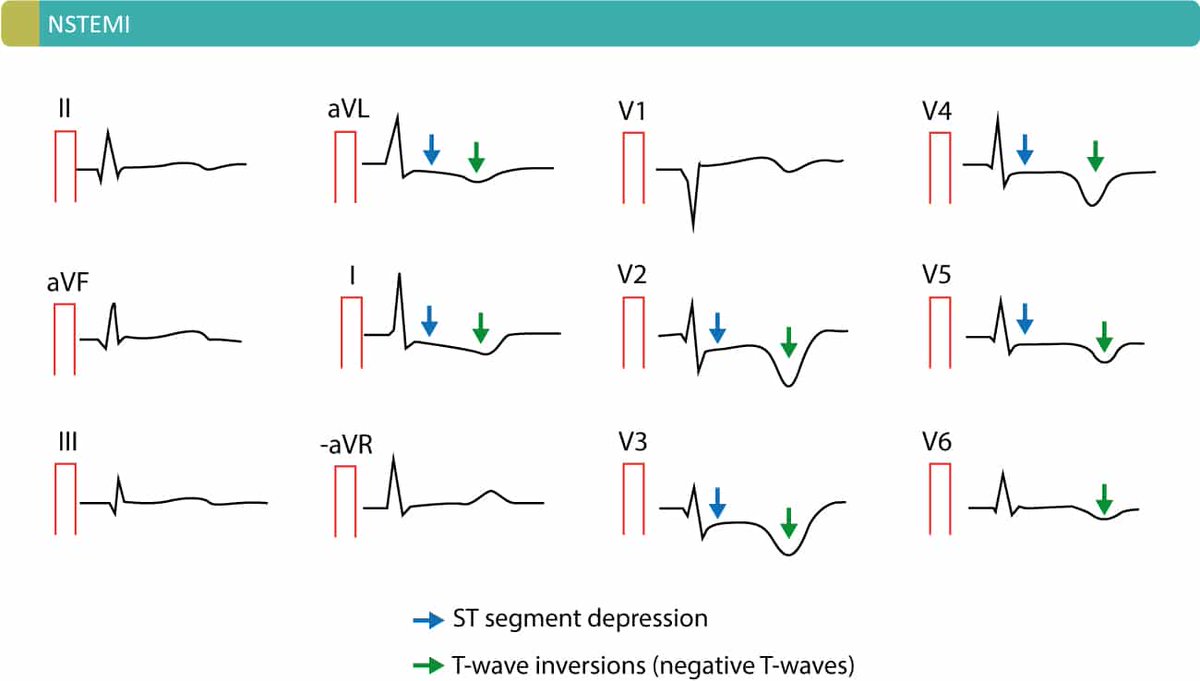
#ثريد ⭕موضوعنا الليله حنشرح فيهو Acute Coronary Syndrome⭕
ريتويت الكل يستفيد🔄فولو ✅وفعل الجرس يوصلك جميع الشروحات اول باول 🔔
بسم الله نبدأ
ريتويت الكل يستفيد🔄فولو ✅وفعل الجرس يوصلك جميع الشروحات اول باول 🔔
بسم الله نبدأ
اول نقطه لازم نعرفها انو ACS عباره عن متلازمه يعني عباره عن مجموعه من الامراض واحد من الامراض دي بجينا باعراض ACS
⭕Definition :
It's a term that used to describe arange of conditions associated with sudden reduce blood flow to the heart
⭕Definition :
It's a term that used to describe arange of conditions associated with sudden reduce blood flow to the heart
Include unstable angina & myocardial infarction these share a common underlying pathology plaque rubture thrombosis and inflammation rarely caused by emboli
Myocardial infarction mean there's myocardial cell deathe result release of troponin
عشان كدا لما يجينا مريض باعراض ACS بنعمل ليهو ECG ونطلب ليهو cardiac markers
⭕Symptoms :
Acute central chest pain lasting more than 20 min
Associated with nausea, dyspnea sweatiness,palpitation
عشان كدا لما يجينا مريض باعراض ACS بنعمل ليهو ECG ونطلب ليهو cardiac markers
⭕Symptoms :
Acute central chest pain lasting more than 20 min
Associated with nausea, dyspnea sweatiness,palpitation
ACS ممكن يجيك بدون اعراض ودي بنسميها Silent MI
ودي بنشوفها في الناس الكبار Elderly والناس العندهم سكري DM
Silent MI may be present with syncope and polmunary edema, epigastric pain
نركز هنا لانو الخطأ دا بقعو فيهو كميه من الدكاتره اذا جاك مريض ويشكي من epigastric pain
ودي بنشوفها في الناس الكبار Elderly والناس العندهم سكري DM
Silent MI may be present with syncope and polmunary edema, epigastric pain
نركز هنا لانو الخطأ دا بقعو فيهو كميه من الدكاتره اذا جاك مريض ويشكي من epigastric pain
اول حاجه تشوف عمرو كم وهل عندو سكري او لا لانو ديل ال MI بتظهر ليهم كدا بجيك يقول لسك عندي الم في معدتي بس خت في بالك دايما silent MI
⭕Signs:
Distress, anxiety, pallor, sweatiness, hight BP, pulse increase or decrease, 4th heart sound
ممكن يجيك بعلامات heart failuer
Increase JVP, 3rd heart sound, basal crepitation
Or
pan systolic murmur ودي بتكون بسبب papillary muscle rupture or VSD
Distress, anxiety, pallor, sweatiness, hight BP, pulse increase or decrease, 4th heart sound
ممكن يجيك بعلامات heart failuer
Increase JVP, 3rd heart sound, basal crepitation
Or
pan systolic murmur ودي بتكون بسبب papillary muscle rupture or VSD
وعشان نشخصو بكون clinical assessment and troponin test
2- on chest x-ray
Cardiomegaly, polmunary edema or widened mediastinum
3- Echo cardiogram
Regional wall abnormality
2- on chest x-ray
Cardiomegaly, polmunary edema or widened mediastinum
3- Echo cardiogram
Regional wall abnormality
⭕Differential diagnoses :
Stable angina, pericaritis, myocarditis, aortic dissection, musculoskeletal pain
Mortality rate 50% of death occur within 2 hours of omset of symptoms
7% die before discharge
Worse prognosis if elderly, left ventricular failure, st changes
Stable angina, pericaritis, myocarditis, aortic dissection, musculoskeletal pain
Mortality rate 50% of death occur within 2 hours of omset of symptoms
7% die before discharge
Worse prognosis if elderly, left ventricular failure, st changes
Troponins are proteins involved in cardiac and skeletal muscle contraction When myocardial cells are damaged, troponins are released and en-
ter the bloodstream. The levels of troponin in the blood can therefore help with
diagnosing myocardial damage.
ter the bloodstream. The levels of troponin in the blood can therefore help with
diagnosing myocardial damage.
Troponins I and T are most specifi c to the heart.
Troponin levels are most commonly measured when ACS is suspected
Troponin levels are most commonly measured when ACS is suspected
⭕Management :
العلاج بعتمد اول شي على معرفة هل في STEMI او لا
Manage chest pain with PRN GTN and opiates.If this proves insuffi cient,consider a
GTN infusion(monitor BP,omit if recent sildenafi l use).If pain is deteriorating,seek
senior help.Manage symptomatic heart failure
العلاج بعتمد اول شي على معرفة هل في STEMI او لا
Manage chest pain with PRN GTN and opiates.If this proves insuffi cient,consider a
GTN infusion(monitor BP,omit if recent sildenafi l use).If pain is deteriorating,seek
senior help.Manage symptomatic heart failure
Modify risk factors
• Patients should be strongly advised and helped to stop smoking
• Identify and treat diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidaemia.
• Advise a diet high in oily fi sh, fruit, vegetables, & fi bre, and low in saturated fats
• Patients should be strongly advised and helped to stop smoking
• Identify and treat diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidaemia.
• Advise a diet high in oily fi sh, fruit, vegetables, & fi bre, and low in saturated fats
• Encourage daily exercise. Refer to a cardiac rehab programme.
• Mental health: flag to the patient’s GP if depression or anxiety are present—these
are independently associated with poor cardiovascular outcomes.
• Mental health: flag to the patient’s GP if depression or anxiety are present—these
are independently associated with poor cardiovascular outcomes.
Optimize cardioprotective medications
• Antiplatelets: aspirin (75mg OD) and a second antiplatelet agent (eg clopidogrel)
for at least 12 months to vascular events (eg MI, stroke). Consider adding a PPI (eg
lansoprazole) for gastric protection.
• Antiplatelets: aspirin (75mg OD) and a second antiplatelet agent (eg clopidogrel)
for at least 12 months to vascular events (eg MI, stroke). Consider adding a PPI (eg
lansoprazole) for gastric protection.
• Anticoagulate, eg with fondaparinux, until discharge.
• -blockade reduces myocardial oxygen demand. Start low and increase slowly,
monitoring pulse and BP. If contraindicated, consider verapamil or diltiazem.
• -blockade reduces myocardial oxygen demand. Start low and increase slowly,
monitoring pulse and BP. If contraindicated, consider verapamil or diltiazem.
• ACE-i in patients with LV dysfunction, hypertension, or diabetes unless not tolerated
(consider ARB). Titrate up slowly, monitoring renal function.
• High-dose statin, eg atorvastatin 80mg.
(consider ARB). Titrate up slowly, monitoring renal function.
• High-dose statin, eg atorvastatin 80mg.
• Do an echo to assess LV function. Eplerenone improves outcomes in MI patients
with heart failure (ejection fraction <40%).
with heart failure (ejection fraction <40%).
Revascularization
• STEMI patients and very high-risk NSTEMI patients (eg haemodynamically unstable)
should receive immediate angiography ± PCI. NSTEMI patients who are high risk
• STEMI patients and very high-risk NSTEMI patients (eg haemodynamically unstable)
should receive immediate angiography ± PCI. NSTEMI patients who are high risk
should receive immediate angiography ± PCI. NSTEMI patients who are high risk (eg
GRACE score >140) should have angiography within 24h
GRACE score >140) should have angiography within 24h
intermediate risk (eg GRACE
109–140) within 3d; low-risk patients may be considered for non-invasive testing.
• Patients with multivessel disease may be considered for CABG instead of PCI
109–140) within 3d; low-risk patients may be considered for non-invasive testing.
• Patients with multivessel disease may be considered for CABG instead of PCI
Discharge Address any questions the patient has. Discuss ‘red flag’ symptoms and
where to seek medical advice should they arise. Ensure the management plan is
communicated to the patient’s GP. Book clinic and cardiac rehab appointments.
where to seek medical advice should they arise. Ensure the management plan is
communicated to the patient’s GP. Book clinic and cardiac rehab appointments.
⭕Complications of MI :
Cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, left ventricular failure, Bradyarrhythmia, tachyarrytmia, right ventricular failure, pericaritis,
Cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, left ventricular failure, Bradyarrhythmia, tachyarrytmia, right ventricular failure, pericaritis,
كدا انتهينا من شرح ACS اتمنى يكون واضح
اي زول عندو سؤال DM
ريتويت الكل يستفيد 🔄فولو✅فعل الجرس يوصلك كل الشروحات والملخصات 🔔
بالتوفيق لكم جميعا 🙏
اي زول عندو سؤال DM
ريتويت الكل يستفيد 🔄فولو✅فعل الجرس يوصلك كل الشروحات والملخصات 🔔
بالتوفيق لكم جميعا 🙏
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...