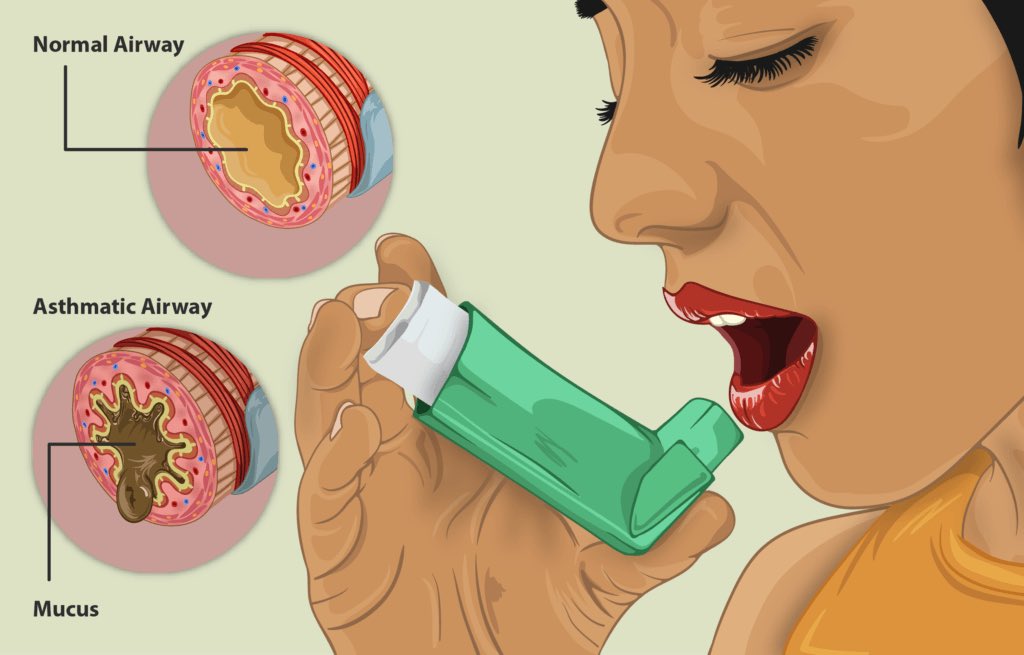
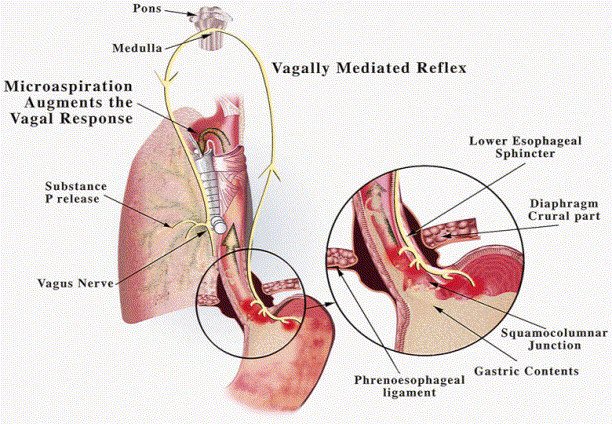
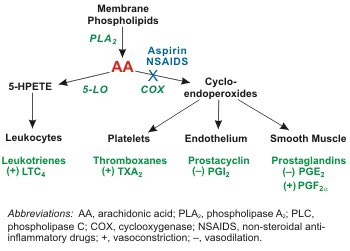
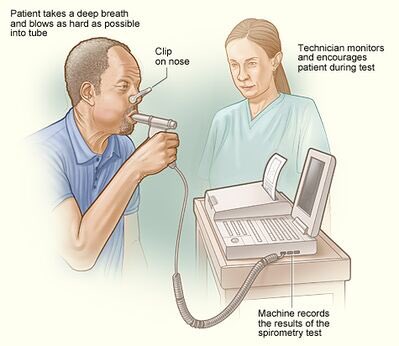
Pathophysiology:
Allergen bind to (T-helper ll cells) release:
•interleukin-4
•interleukin-5
•interleukin-4 activate plasma to release more (IgE) it’s bind to mast cells to release histamine and leukotrienes.
•interleukin-5 eosinophils to release leukotrienes and proteases.
Allergen bind to (T-helper ll cells) release:
•interleukin-4
•interleukin-5
•interleukin-4 activate plasma to release more (IgE) it’s bind to mast cells to release histamine and leukotrienes.
•interleukin-5 eosinophils to release leukotrienes and proteases.
Treatment:
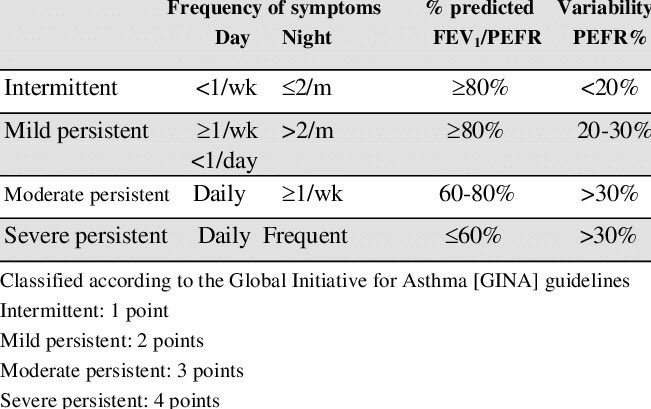
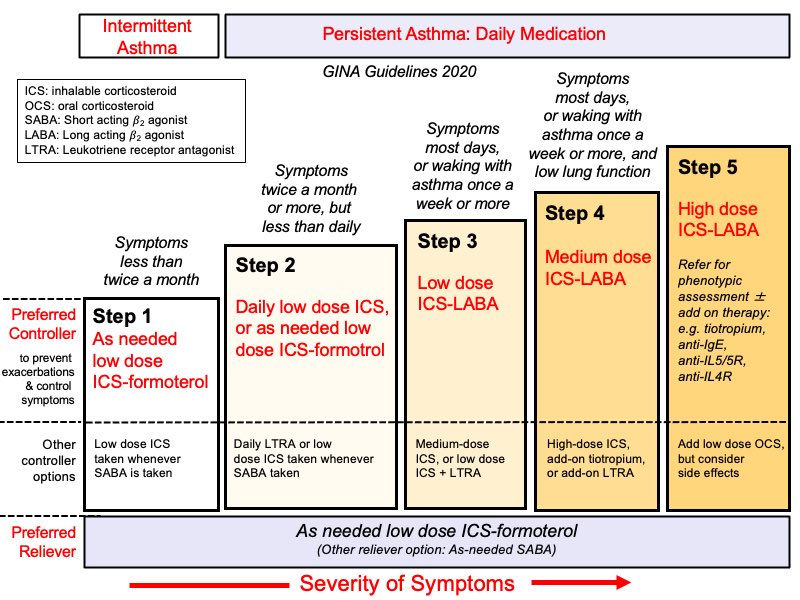
1-intermittent (SABA) short acting beta2 agonist.
2-mild persistent (SABA + low dose of inhaled corticosteroid ICS).
3-moderate persistent (SABA + medium dose ICS).
or (SABA + low dose of ICS + LABA long acting beta2 agonist).
1-intermittent (SABA) short acting beta2 agonist.
2-mild persistent (SABA + low dose of inhaled corticosteroid ICS).
3-moderate persistent (SABA + medium dose ICS).
or (SABA + low dose of ICS + LABA long acting beta2 agonist).
4-severe persistent:
1- SABA + medium dose ICS + LABA
If doesn’t work
2-SABA + high dose ICS + LABA
If doesn’t work
3-SABA + high dose ICS + LABA + oral corticosteroid
1- SABA + medium dose ICS + LABA
If doesn’t work
2-SABA + high dose ICS + LABA
If doesn’t work
3-SABA + high dose ICS + LABA + oral corticosteroid
If doesn’t work
2-SABA + Ipratropium bromide (muscrinic receptor antagonist).
If doesn’t work
3-IV or PO corticosteroids
2-SABA + Ipratropium bromide (muscrinic receptor antagonist).
If doesn’t work
3-IV or PO corticosteroids
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...