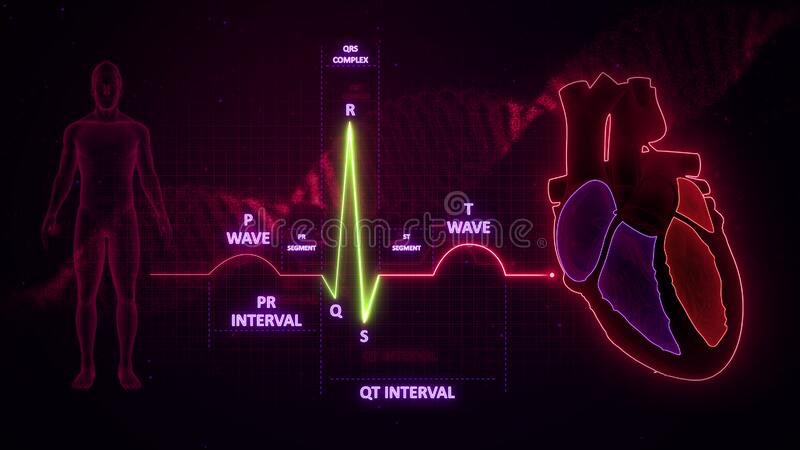
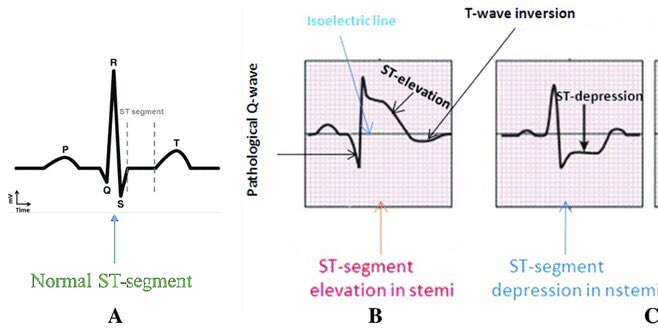
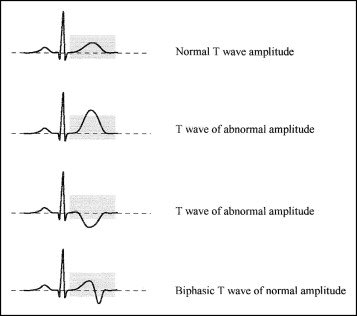
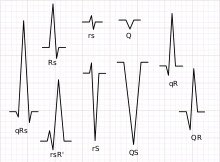
First (S-T segment elevation):
1mm S-T elevation in all leads except V2, V3 is considered S-T elevation.
2mm S-T elevation in V2,V3 is considered ➡️ S-T elevation.
DDx:
-STEMI
-Benign early repolarization
-pericarditis
-vassospasms
-PE
-left ventricle aneurysm
-LVH
-LBBB
1mm S-T elevation in all leads except V2, V3 is considered S-T elevation.
2mm S-T elevation in V2,V3 is considered ➡️ S-T elevation.
DDx:
-STEMI
-Benign early repolarization
-pericarditis
-vassospasms
-PE
-left ventricle aneurysm
-LVH
-LBBB
Second (S-T depression):
<0.5 mm of S-T depression in any lead ➡️ S-T depression.
Types:
Down-sloping
Up-sloping
Horizontal (more considered as ischemia)
Note 📝 up-sloping in V1-V3 with peaked T wave ➡️ proximal left anterior descending artery occlusion (LAD).
<0.5 mm of S-T depression in any lead ➡️ S-T depression.
Types:
Down-sloping
Up-sloping
Horizontal (more considered as ischemia)
Note 📝 up-sloping in V1-V3 with peaked T wave ➡️ proximal left anterior descending artery occlusion (LAD).
DDx:
⁃NSTEMI
⁃Posterior MI
⁃LBBB
⁃Left ventricle hypertrophy with strain pattern
⁃Reciprocal changes
⁃Digoxin toxicity
⁃NSTEMI
⁃Posterior MI
⁃LBBB
⁃Left ventricle hypertrophy with strain pattern
⁃Reciprocal changes
⁃Digoxin toxicity
Third (J wave present):
DDX:
⁃Benign early repolrization
⁃hypothermia
⁃hypercalcemia
⁃Brugada syndrome
DDX:
⁃Benign early repolrization
⁃hypothermia
⁃hypercalcemia
⁃Brugada syndrome
First (T wave inversion):
> or equal 1mm of T-wave depression.
T wave inversion is normal in V1, V2 and lead lll.
DDx:
⁃Left ventricle strain (hypertrophy)
⁃Increase ICP
⁃PE
⁃bundle branch block
⁃Wellen’s syndrome B in V2 and V3 (ischemia)
⁃Inferior MI
> or equal 1mm of T-wave depression.
T wave inversion is normal in V1, V2 and lead lll.
DDx:
⁃Left ventricle strain (hypertrophy)
⁃Increase ICP
⁃PE
⁃bundle branch block
⁃Wellen’s syndrome B in V2 and V3 (ischemia)
⁃Inferior MI
Note 📝 T wave inversion in aVL is only suspicion of Inferior MI.
Second (hyperacute T-wave):
Tall and asymmetrical peak can equal QRS complex.
DDx:
⁃vasospasm (prinzmetal angina) is spasm in coronary artery.
⁃Early STEMI
Tall and asymmetrical peak can equal QRS complex.
DDx:
⁃vasospasm (prinzmetal angina) is spasm in coronary artery.
⁃Early STEMI
Third (Biphasic T-wave):
Initial positive deflection followed by negative deflection, It might be the other way around.
DDx:
⁃(Wellen’s A) ischemia
⁃Hyperkalemia
Initial positive deflection followed by negative deflection, It might be the other way around.
DDx:
⁃(Wellen’s A) ischemia
⁃Hyperkalemia
Fourth (flat T-wave):
Between -1 and 1 mm deflection
DDx:
⁃ischemia
⁃Hyperkalemia
Between -1 and 1 mm deflection
DDx:
⁃ischemia
⁃Hyperkalemia
Fifth (peaked T-wave):
Very tall, very narrow and symmetrical peak.
DDx:
⁃hyperkalemia
⁃Hypermagnesemia
⁃Ischemia (D-wniters Twave)
Note 📝 D winters with up-sloping S-T depression is considered as proximal LAD.
Very tall, very narrow and symmetrical peak.
DDx:
⁃hyperkalemia
⁃Hypermagnesemia
⁃Ischemia (D-wniters Twave)
Note 📝 D winters with up-sloping S-T depression is considered as proximal LAD.
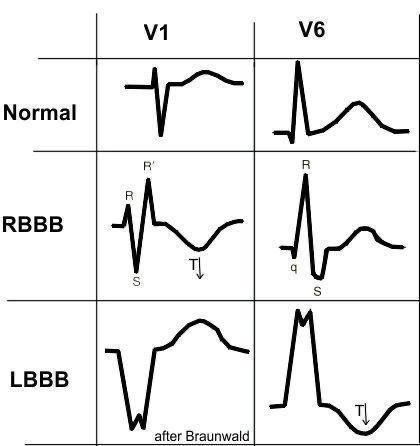
First (wide QRS):
> 0.12 sec is wide QRS
DDx:
⁃BBB
⁃Hyperkalemia
⁃V tach
⁃WPW
⁃Paced rhythm (pt on pacemaker)
⁃Medication (tricyclic, antidepressants overdose).
> 0.12 sec is wide QRS
DDx:
⁃BBB
⁃Hyperkalemia
⁃V tach
⁃WPW
⁃Paced rhythm (pt on pacemaker)
⁃Medication (tricyclic, antidepressants overdose).
Second (Q wave):
If you see Q wave in V1 and V3 ➡️it’s not normal
Pathological Q wave:
⁃> 0.04 sec
⁃2mm in depth
⁃25% of QRS length
DDx:
⁃MI
⁃PE
⁃LBBB
⁃Left ventricle hypertrophy
If you see Q wave in V1 and V3 ➡️it’s not normal
Pathological Q wave:
⁃> 0.04 sec
⁃2mm in depth
⁃25% of QRS length
DDx:
⁃MI
⁃PE
⁃LBBB
⁃Left ventricle hypertrophy
Third (low voltage QRS):
How to detect low voltage QRS:
1- add up leads I, II, lll
If it’s < 15mm ➡️ low voltage
Or
2- add up V1, V2, V3
If it’s < 30mm ➡️ low voltage
How to detect low voltage QRS:
1- add up leads I, II, lll
If it’s < 15mm ➡️ low voltage
Or
2- add up V1, V2, V3
If it’s < 30mm ➡️ low voltage
DDx:
(Any reason that block conduction)
⁃pericardial effusion (fluid)
⁃Obesity (fat)
⁃COPD (air)
⁃HF
⁃Infiltrated diseases (rare) for example(amyloidosis and sarcoidosis)
(Any reason that block conduction)
⁃pericardial effusion (fluid)
⁃Obesity (fat)
⁃COPD (air)
⁃HF
⁃Infiltrated diseases (rare) for example(amyloidosis and sarcoidosis)
Fourth (poor R wave progression)
R wave does not increase as expected from V1-V6.
DDx:
⁃anterior MI
⁃Right ventricle hypertrophy
R wave does not increase as expected from V1-V6.
DDx:
⁃anterior MI
⁃Right ventricle hypertrophy
Fifth (dominate R wave):
R wave greater than S wave in V1-V3
DDx:
⁃posterior MI (dominate R wave in V1-V3 with ST depression and upright T wave).
⁃RBBB
⁃Right ventricle hypertrophy
R wave greater than S wave in V1-V3
DDx:
⁃posterior MI (dominate R wave in V1-V3 with ST depression and upright T wave).
⁃RBBB
⁃Right ventricle hypertrophy
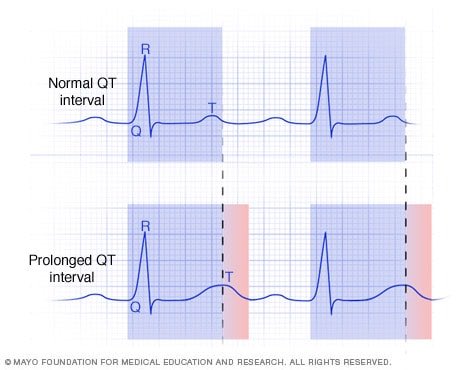
First (prolonged Q-T):
> 460 ms in female
> 450 ms in male
Note 📝 prolonged QT is high risk of torsades de points (polymorphic vtach).
DDx:
⁃anti-arrhythmic
⁃Antibiotics
⁃Antipsychotic
⁃Antidepressants
⁃Antiemetic
⁃Hypokalemia
⁃Hypomagnesemia
⁃Hypocalcemia
> 460 ms in female
> 450 ms in male
Note 📝 prolonged QT is high risk of torsades de points (polymorphic vtach).
DDx:
⁃anti-arrhythmic
⁃Antibiotics
⁃Antipsychotic
⁃Antidepressants
⁃Antiemetic
⁃Hypokalemia
⁃Hypomagnesemia
⁃Hypocalcemia
Second (Short Q-T):
< 350 ms is short QT
DDx:
⁃hyperkalemia
⁃Hypermagnesemia
⁃Digoxin toxicity
< 350 ms is short QT
DDx:
⁃hyperkalemia
⁃Hypermagnesemia
⁃Digoxin toxicity
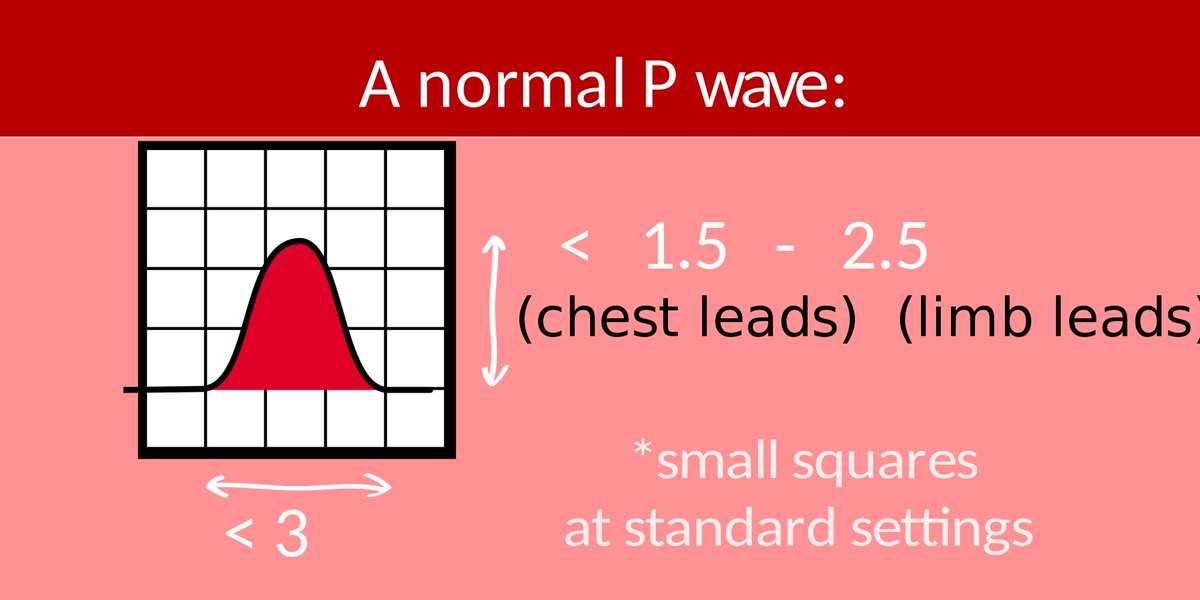
First (right atrial enlargement):
1- in lead ll if p wave > 2.5mm
2- in V1 if positive deflection of p wave > negative deflection of p wave.
DDx:
⁃tricuspid valve stenosis
⁃Pulmonary HTN
⁃Pulmonary valve stenosis
1- in lead ll if p wave > 2.5mm
2- in V1 if positive deflection of p wave > negative deflection of p wave.
DDx:
⁃tricuspid valve stenosis
⁃Pulmonary HTN
⁃Pulmonary valve stenosis
Second (left atrial enlargement):
1- in lead ll if you see p wave bifid (like camel hump 🐫).
2- in V1 if you see negative deflection is > positive deflection.
DDx:
⁃mitral stenosis
⁃Aortic stenosis
⁃HTN
1- in lead ll if you see p wave bifid (like camel hump 🐫).
2- in V1 if you see negative deflection is > positive deflection.
DDx:
⁃mitral stenosis
⁃Aortic stenosis
⁃HTN
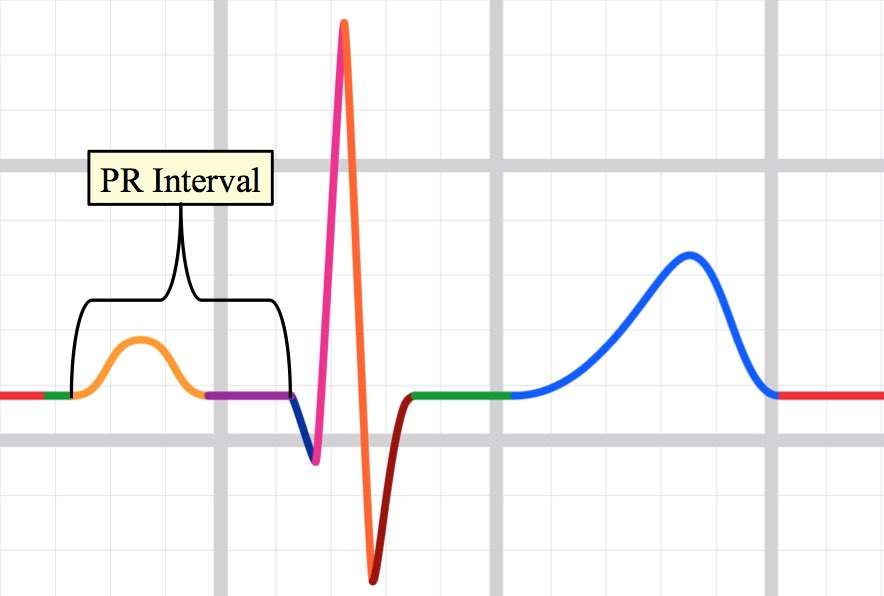
First (short P-R interval):
<0.12s
DDx:
⁃WPW
⁃Premature atrial contraction PAC
<0.12s
DDx:
⁃WPW
⁃Premature atrial contraction PAC
Second (prolonged P-R interval):
>0.20s
DDx:
⁃first degree heart block
⁃Second degree heart block mobitz1
⁃Third degree heart block
>0.20s
DDx:
⁃first degree heart block
⁃Second degree heart block mobitz1
⁃Third degree heart block
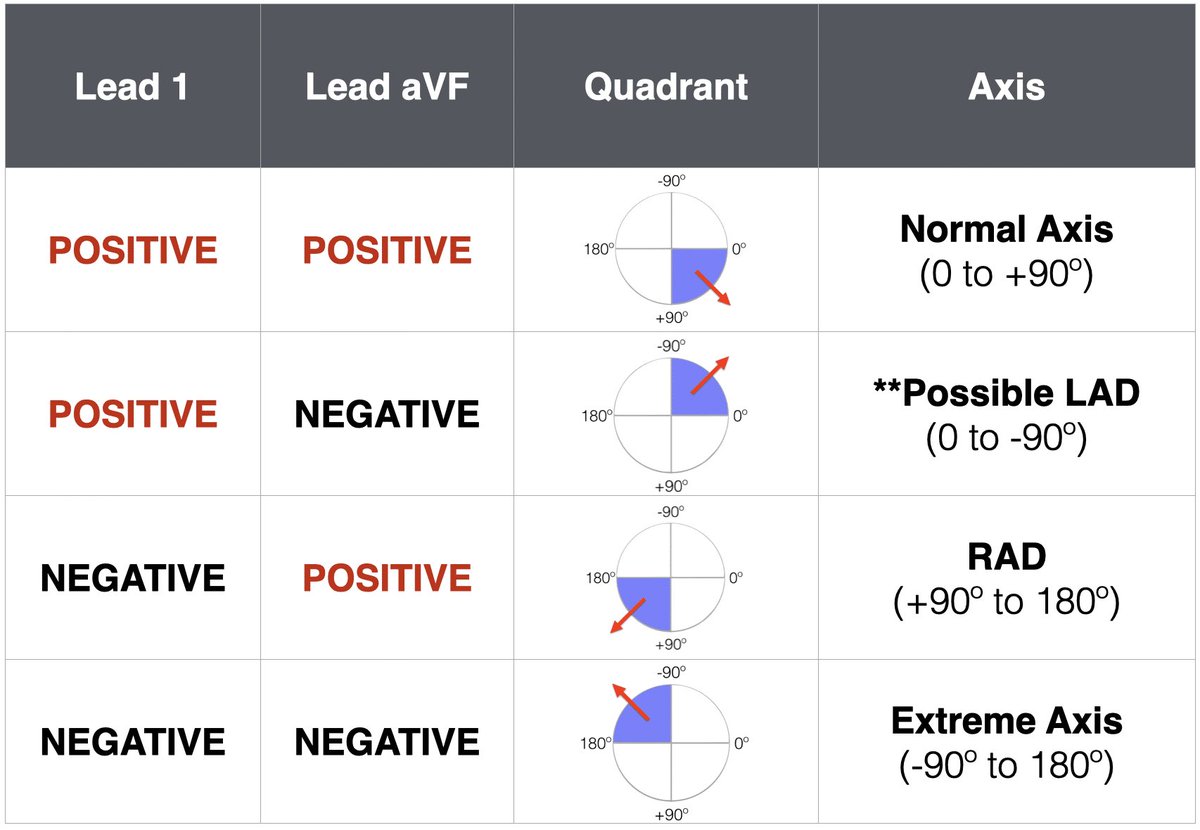
First (left axis deviation):
More electrical activity in lefts side
Lead l positive deflection and aVF negative so you gonna see Lead ll if it’s negative so it’s ➡️ left axis deviation.
DDx:
⁃LBBB
⁃Left ventricle hypertrophy
⁃Inferior MI
⁃Hyperkalemia
More electrical activity in lefts side
Lead l positive deflection and aVF negative so you gonna see Lead ll if it’s negative so it’s ➡️ left axis deviation.
DDx:
⁃LBBB
⁃Left ventricle hypertrophy
⁃Inferior MI
⁃Hyperkalemia
Second (right axis deviation):
Lead l negative deflection
And
aVF positive deflection
DDx:
⁃RBBB
⁃Right ventricle hypertrophy
⁃Anterior MI
⁃V tach
Lead l negative deflection
And
aVF positive deflection
DDx:
⁃RBBB
⁃Right ventricle hypertrophy
⁃Anterior MI
⁃V tach
Third (extreme right axis deviation):
Lead l negative deflection
And
aVF negative deflection
DDx:
⁃extreme right ventricle hypertrophy
⁃V tach
⁃Sever obesity
Lead l negative deflection
And
aVF negative deflection
DDx:
⁃extreme right ventricle hypertrophy
⁃V tach
⁃Sever obesity
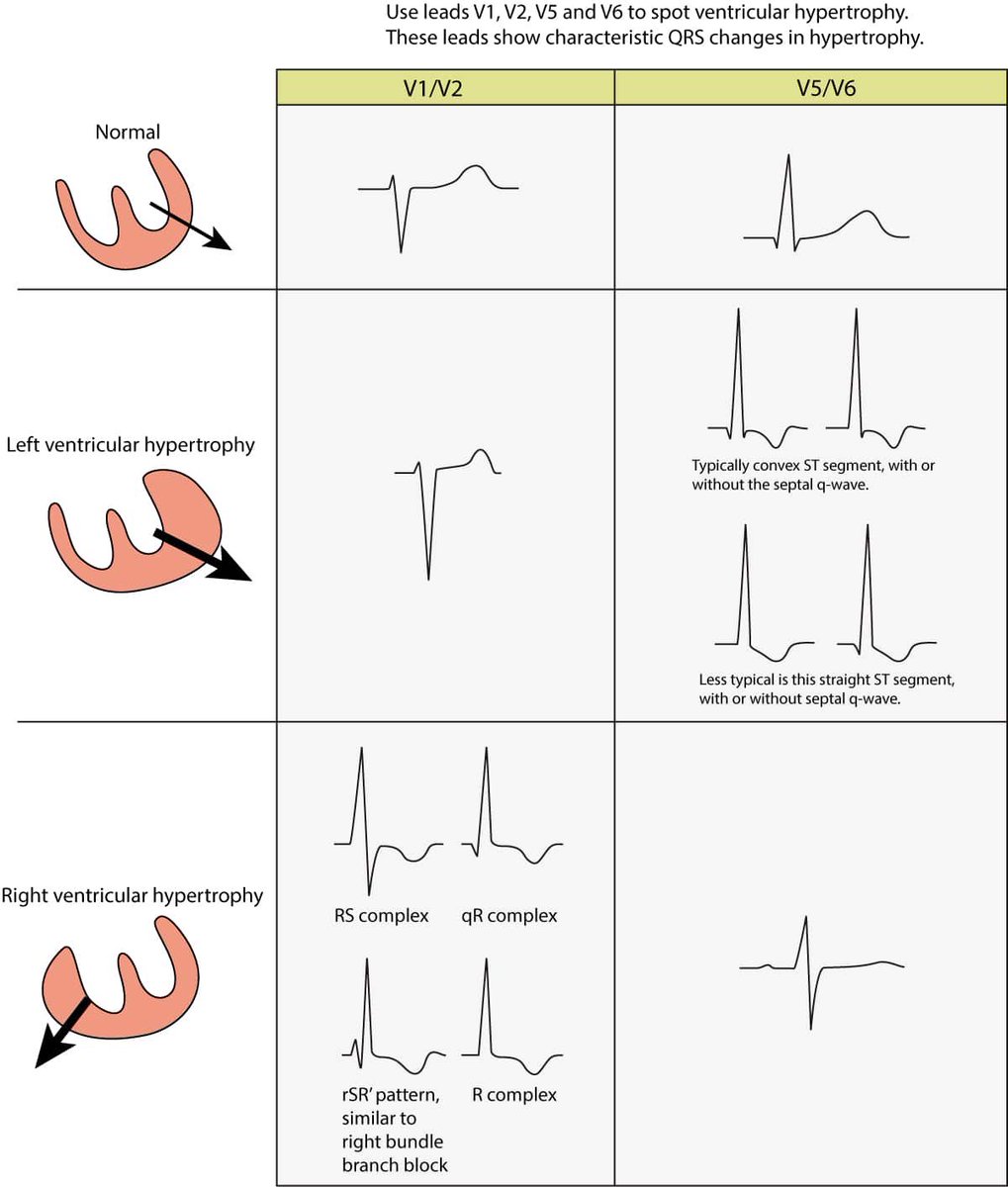
Left ventricle hypertrophy:
If you add up the high of R wave in V5 or V6
To
S wave in V1 or V2 > 35mm ➡️ this left ventricle hypertrophy
Right ventricle hypertrophy:
If you add up R wave in V1 or V2
To
S wave in V5 or V6 > 10mm ➡️ this right ventricle hypertrophy
If you add up the high of R wave in V5 or V6
To
S wave in V1 or V2 > 35mm ➡️ this left ventricle hypertrophy
Right ventricle hypertrophy:
If you add up R wave in V1 or V2
To
S wave in V5 or V6 > 10mm ➡️ this right ventricle hypertrophy
بكذا انتهى الثريد اتمنى انه اعجبكم ❤️
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...