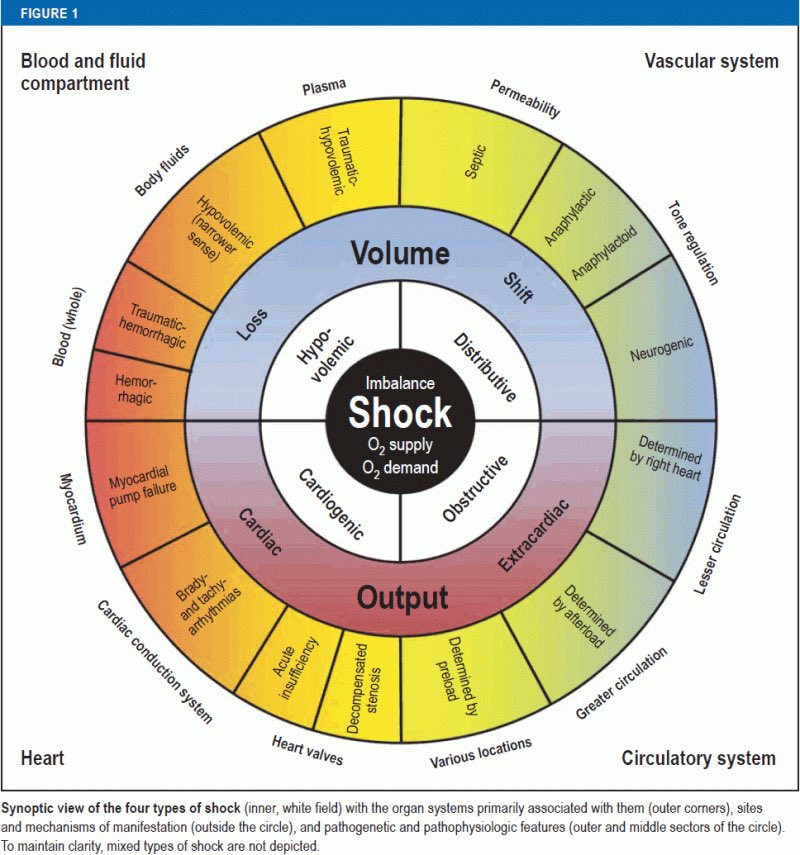
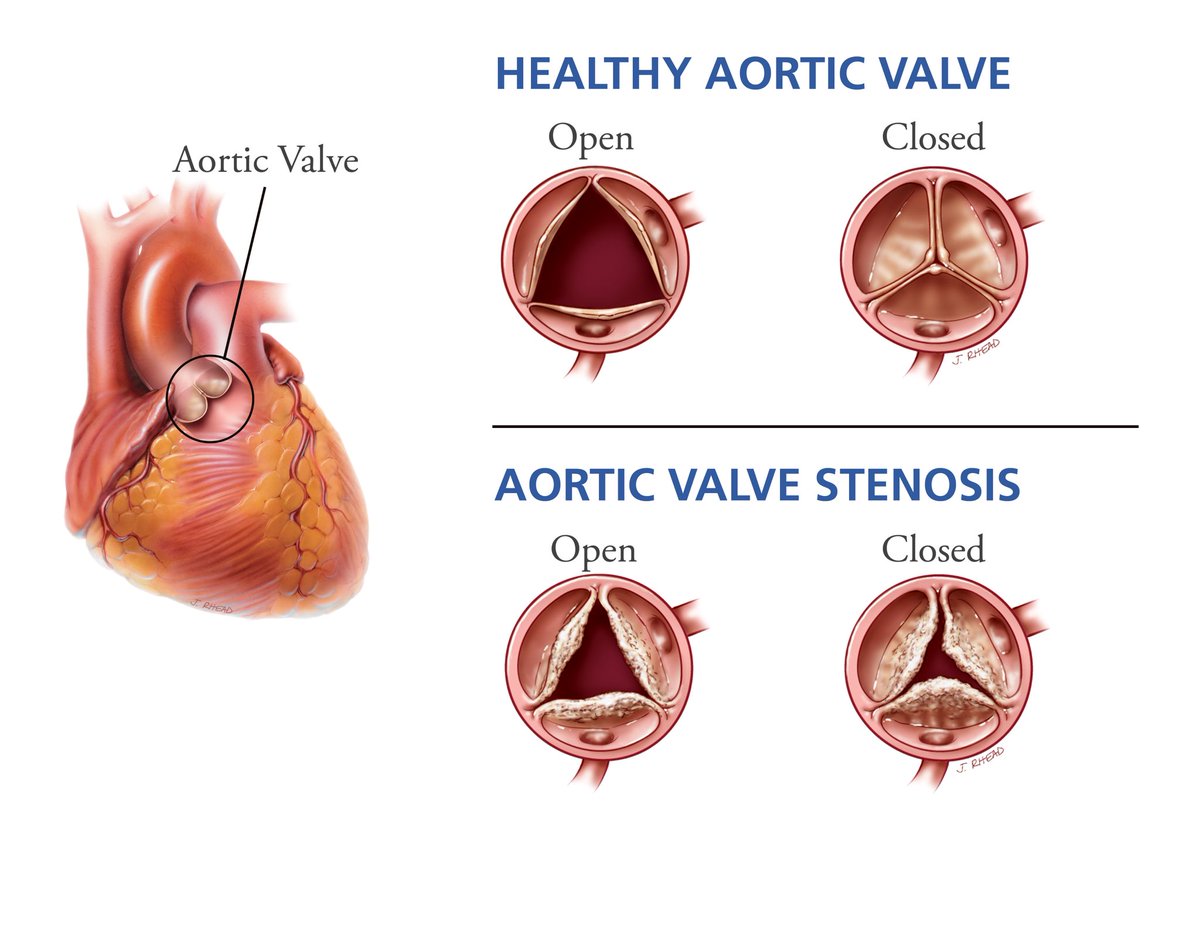
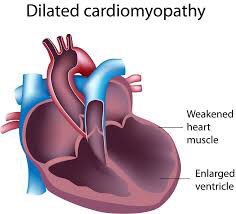
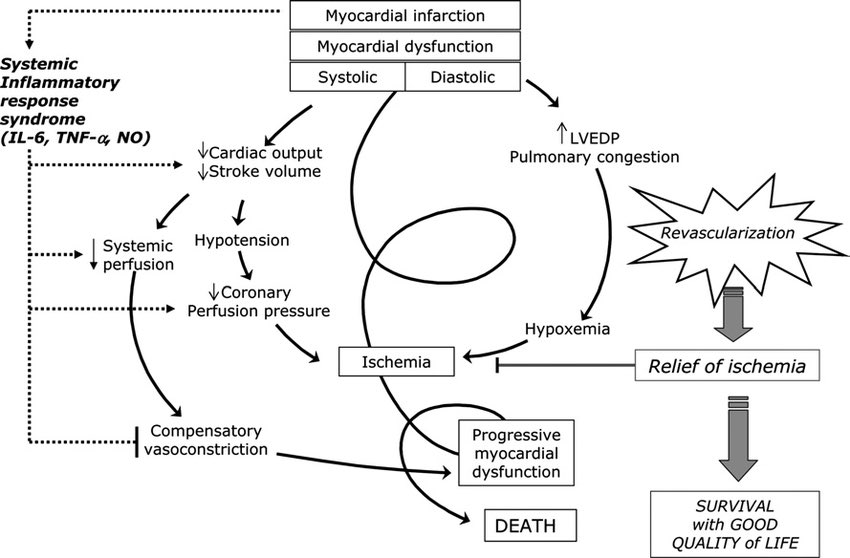
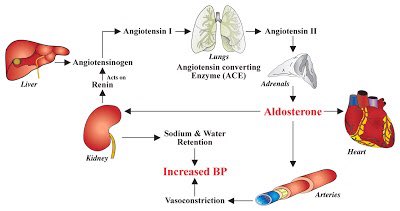
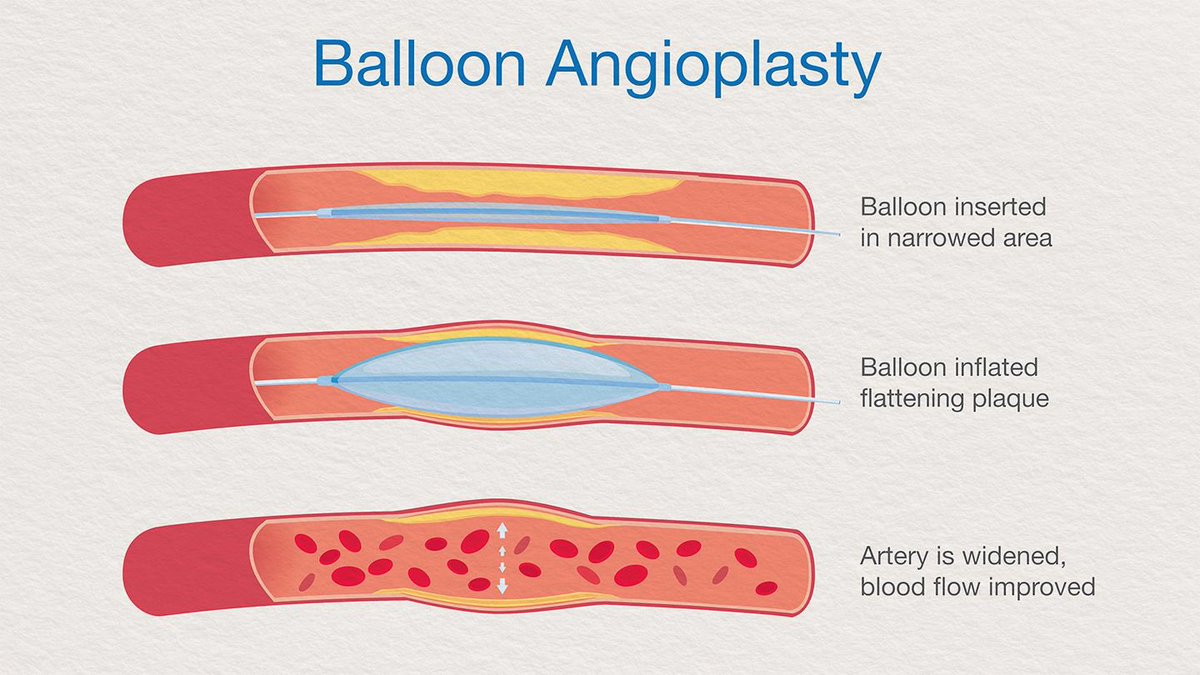
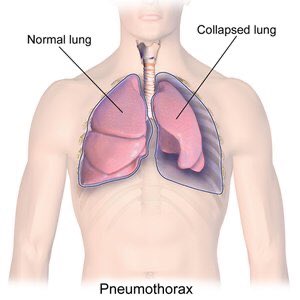
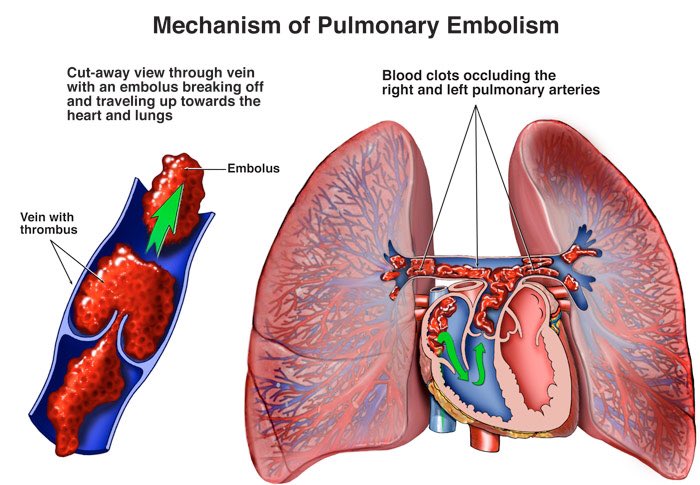
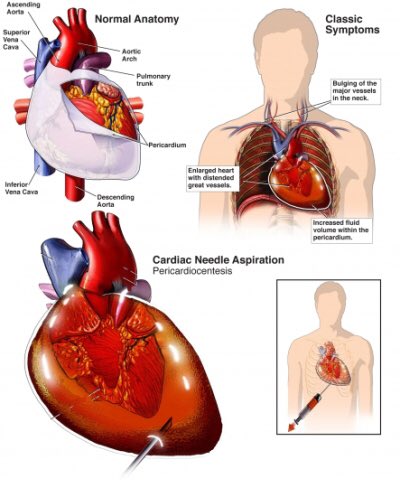
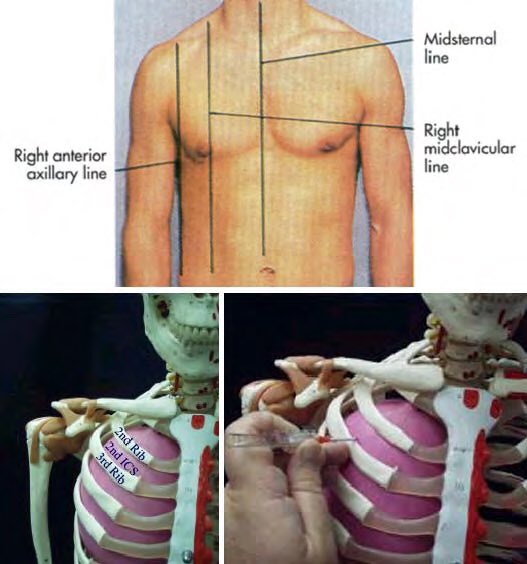
Etiology:
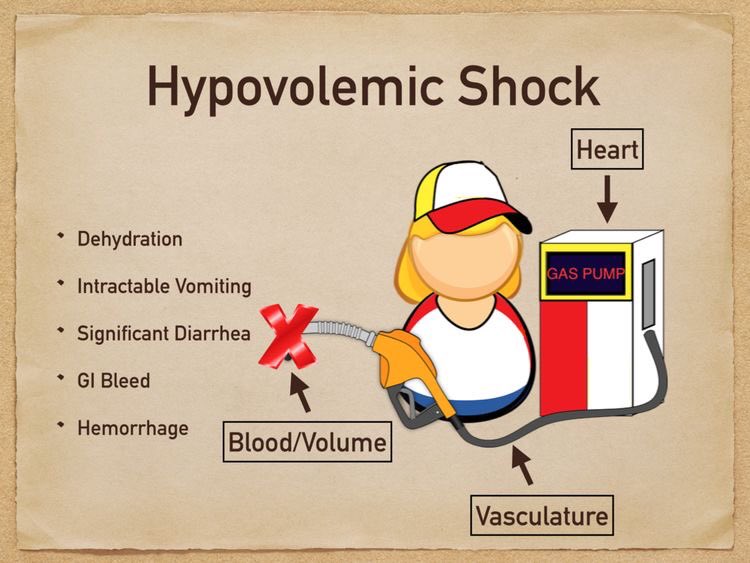
Blood loss (GI bleeding- AAA rupture- Trauma- Postpartum hemorrhage- Ectopic pregnancy- Hemoptysis).
Non blood-fluid loss (3rd degree burn- vomiting- diarrhea- bowel obstruction- Acute pancreatitis- DKA).
Blood loss (GI bleeding- AAA rupture- Trauma- Postpartum hemorrhage- Ectopic pregnancy- Hemoptysis).
Non blood-fluid loss (3rd degree burn- vomiting- diarrhea- bowel obstruction- Acute pancreatitis- DKA).
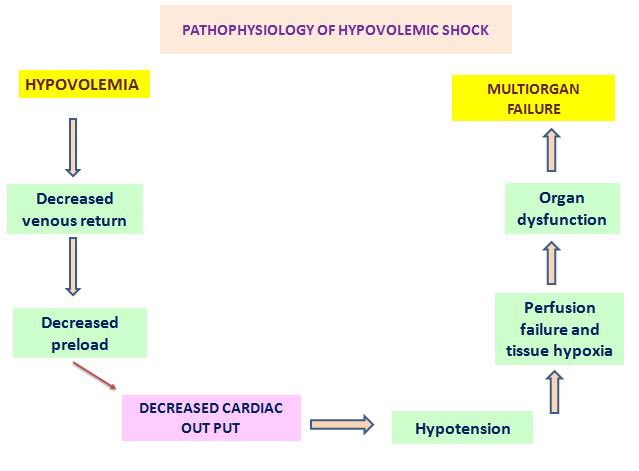
pathophysiology:
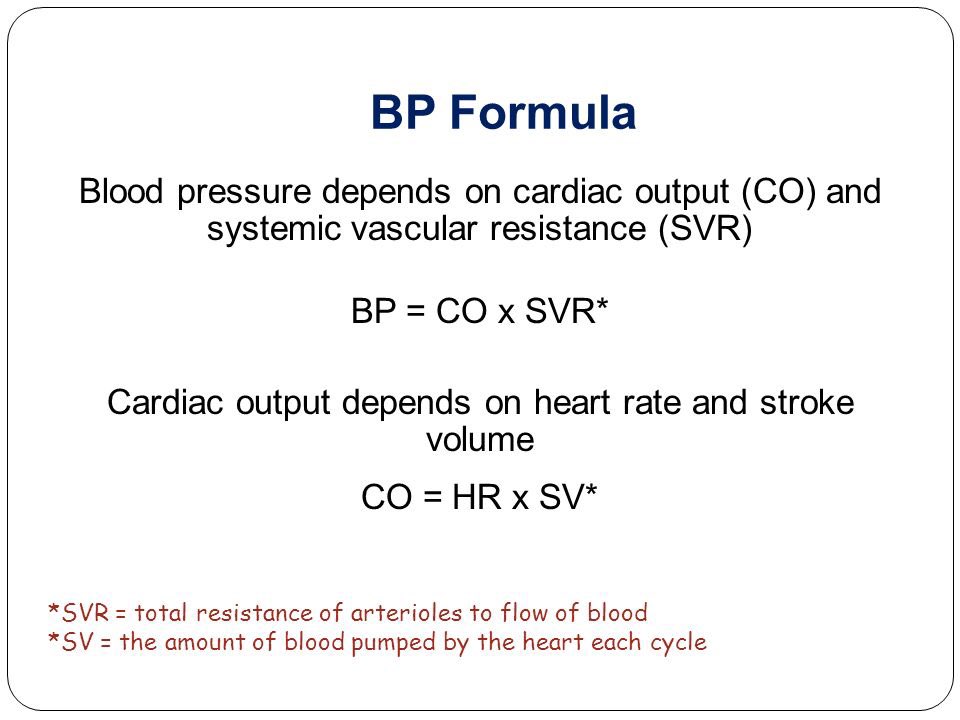
When blood volume decreased the barotrceptors that located in aortic and carotid sinus stimulating the medullary center to send action potentials the goes to:
1-vessels within Tunica media (blood vessels constricted)⬆️ SVR .
When blood volume decreased the barotrceptors that located in aortic and carotid sinus stimulating the medullary center to send action potentials the goes to:
1-vessels within Tunica media (blood vessels constricted)⬆️ SVR .
pathophysiology:
⁃Gram- bacteria has endotoxins damage tissues
⁃Release prostaglandins + leukotriene
⁃Goes to mast cells, and release prostaglandins + leukotriene + proteases + chemotactic agents like histamine.
⁃Gram- bacteria has endotoxins damage tissues
⁃Release prostaglandins + leukotriene
⁃Goes to mast cells, and release prostaglandins + leukotriene + proteases + chemotactic agents like histamine.
The histamine goes to vessels and cause vasodilation + ⬆️ permeability of vessels
⁃Lead to ⬇️ blood volume so ⬇️ BP
⁃chemotactic agents pull more WBC out of vessels to fight bacteria
⁃When this happened some chemicals goes to hypothalamus and increaseTemp.
⁃Lead to ⬇️ blood volume so ⬇️ BP
⁃chemotactic agents pull more WBC out of vessels to fight bacteria
⁃When this happened some chemicals goes to hypothalamus and increaseTemp.
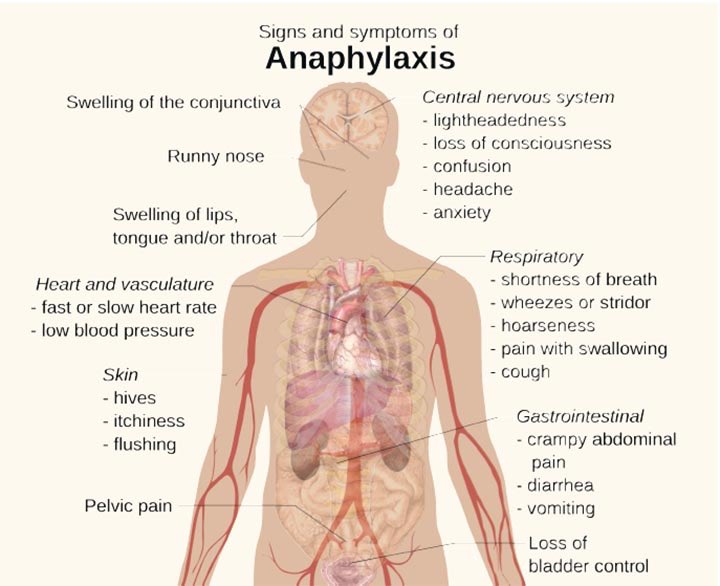
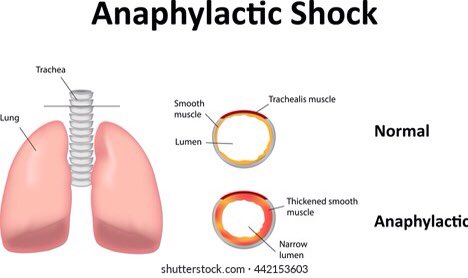
pathophysiology:
⁃allergen bind to mHc-ll receptor on macrophage
⁃Macrophages bind to CDy on T-helper cells (THC)
⁃THC release interleukins ll, lV, V
⁃This stimulates B cells to convert to plasma cell
⁃Plasma cell release antibodies IgE
⁃allergen bind to mHc-ll receptor on macrophage
⁃Macrophages bind to CDy on T-helper cells (THC)
⁃THC release interleukins ll, lV, V
⁃This stimulates B cells to convert to plasma cell
⁃Plasma cell release antibodies IgE
Treatment:
Vasopressors (epinephrine)
Anti-histamine (Benadryl or Ranitidine)
Vasopressors (epinephrine)
Anti-histamine (Benadryl or Ranitidine)
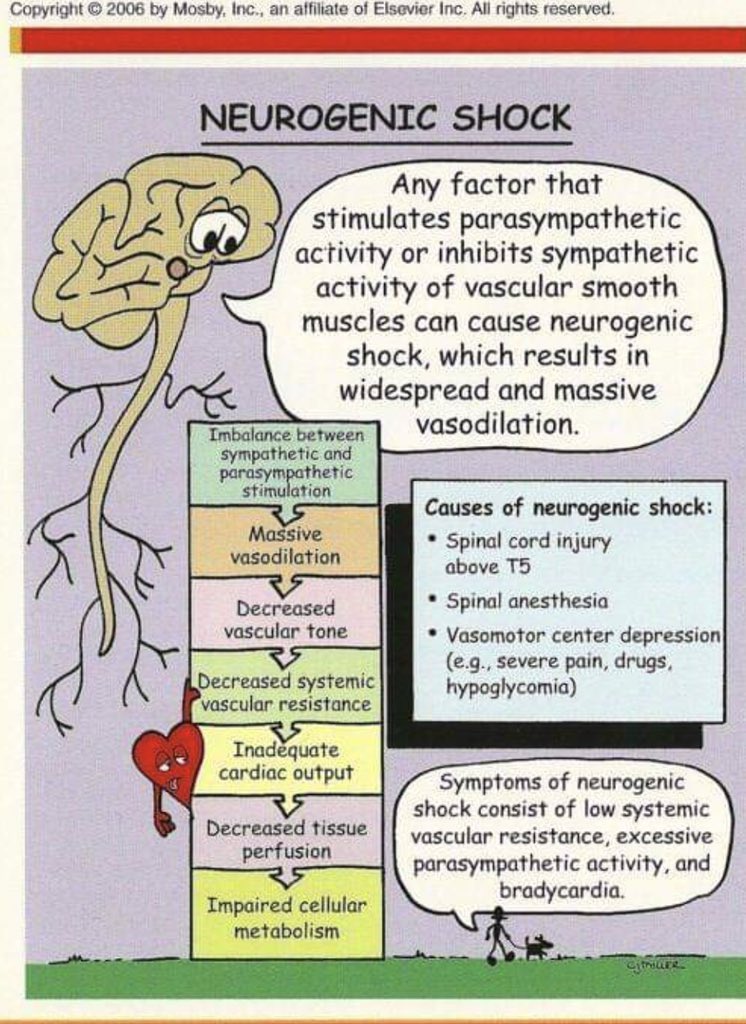
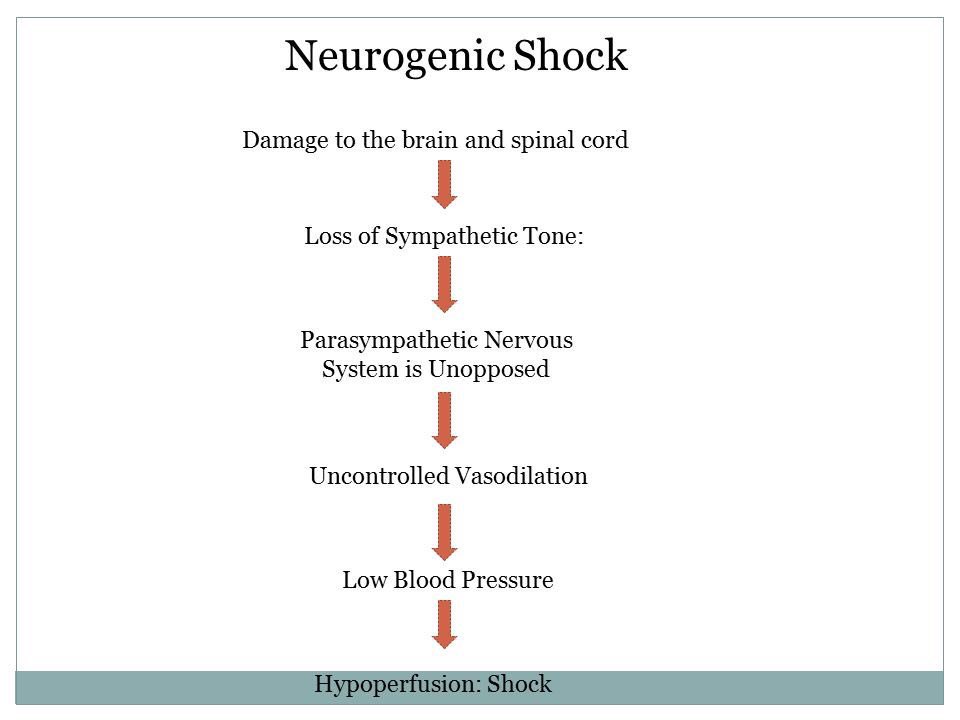
Vasomotor center activities neurons in spinal cord between T1-L2, the information goes to:
1-the heart (SA, AV node and the myocardium). Cause increase heart rate + chronotropic and increase contractility +inotropic
2-blood vessels cause vasoconstriction
1-the heart (SA, AV node and the myocardium). Cause increase heart rate + chronotropic and increase contractility +inotropic
2-blood vessels cause vasoconstriction
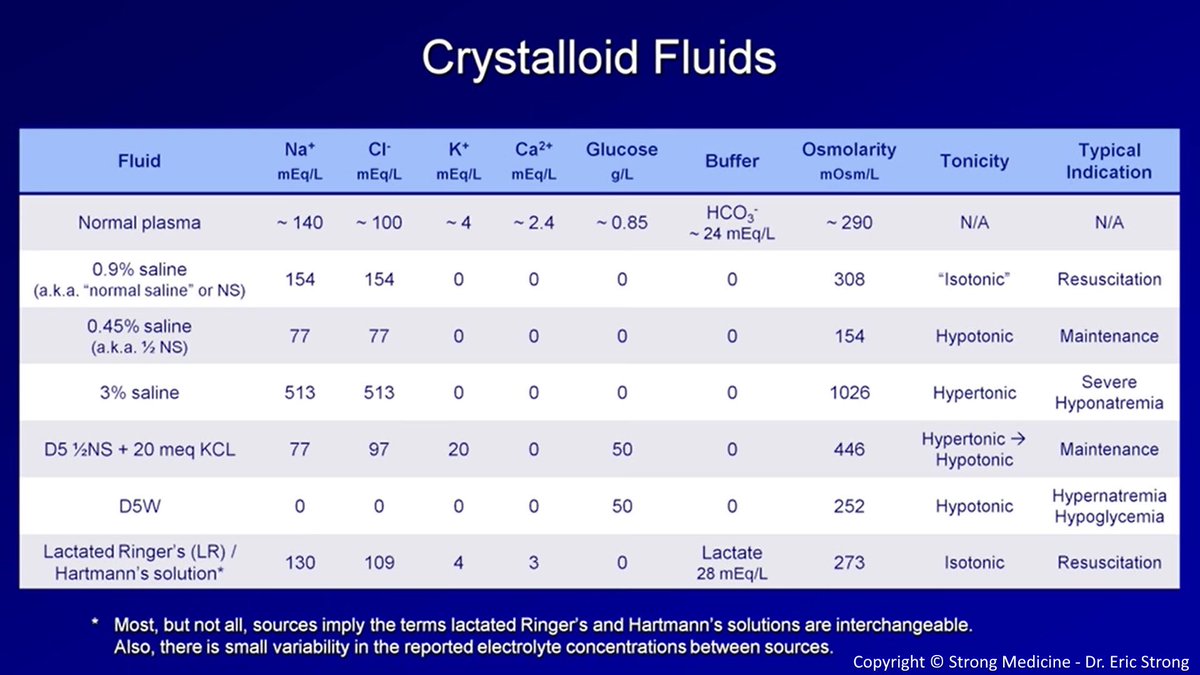
Treatment:
Iv fluids
Vasopressors:
-Dobutamine
-Epinephrine
-Atropine
Note 📝 sometimes you can use corticosteroids.
Iv fluids
Vasopressors:
-Dobutamine
-Epinephrine
-Atropine
Note 📝 sometimes you can use corticosteroids.
بكذا انتهى الثريد للي حاب يطلع اكثر ، تركتلك هذا الرابط راح يفيدك كثير 🙏❤️
amboss.com
amboss.com
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...