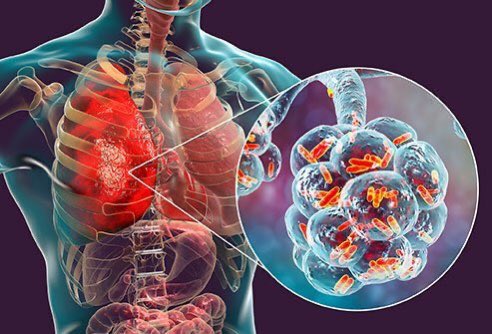
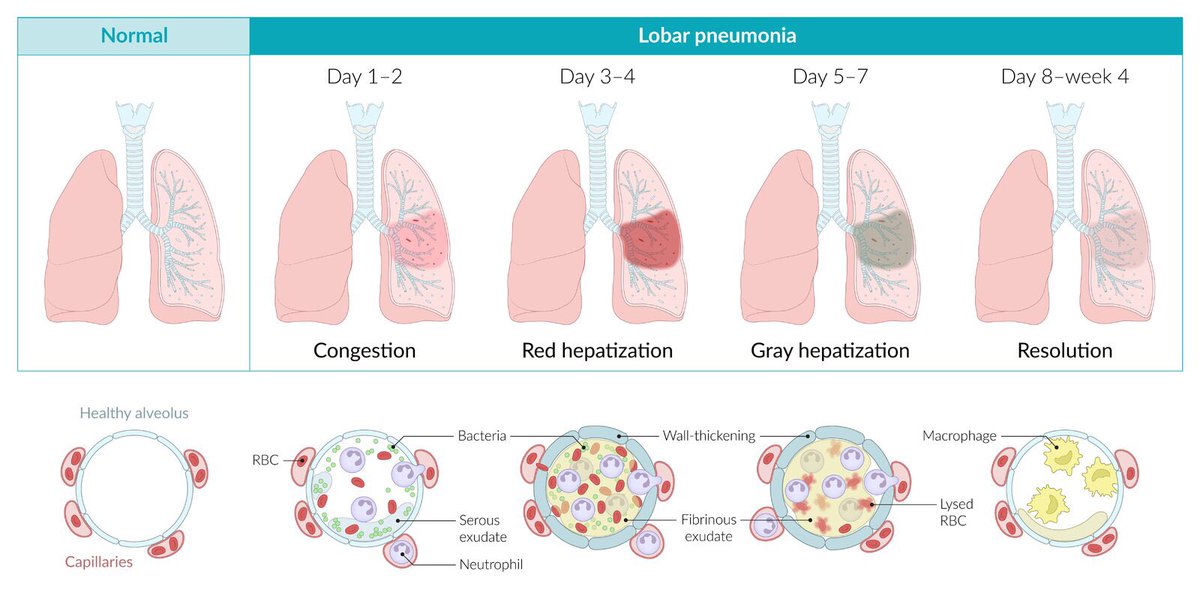
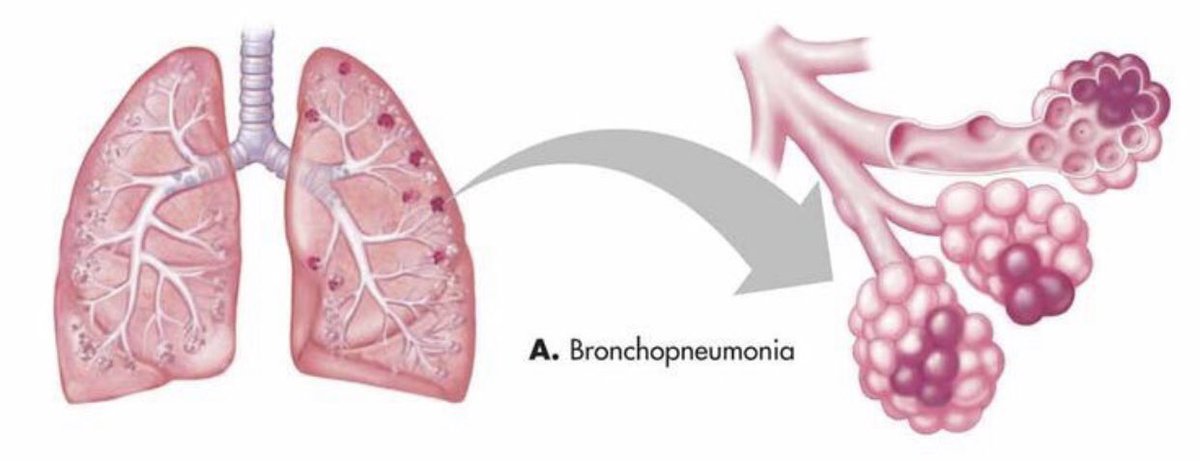
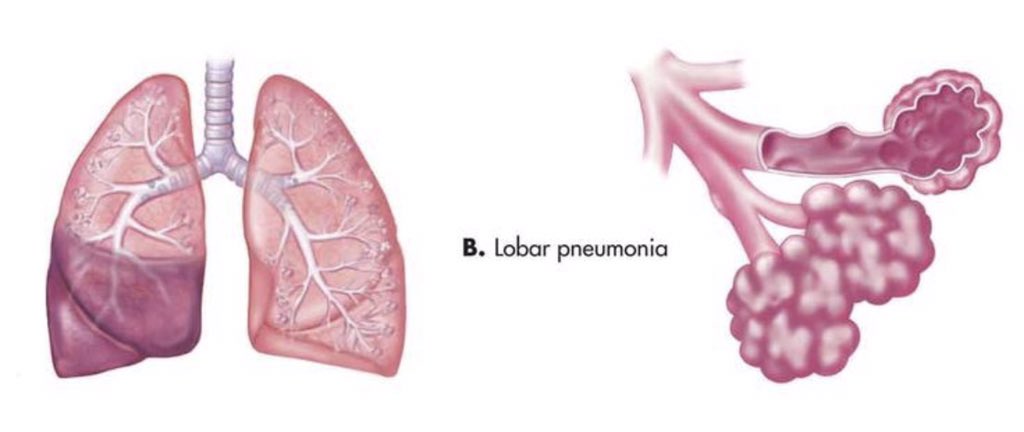
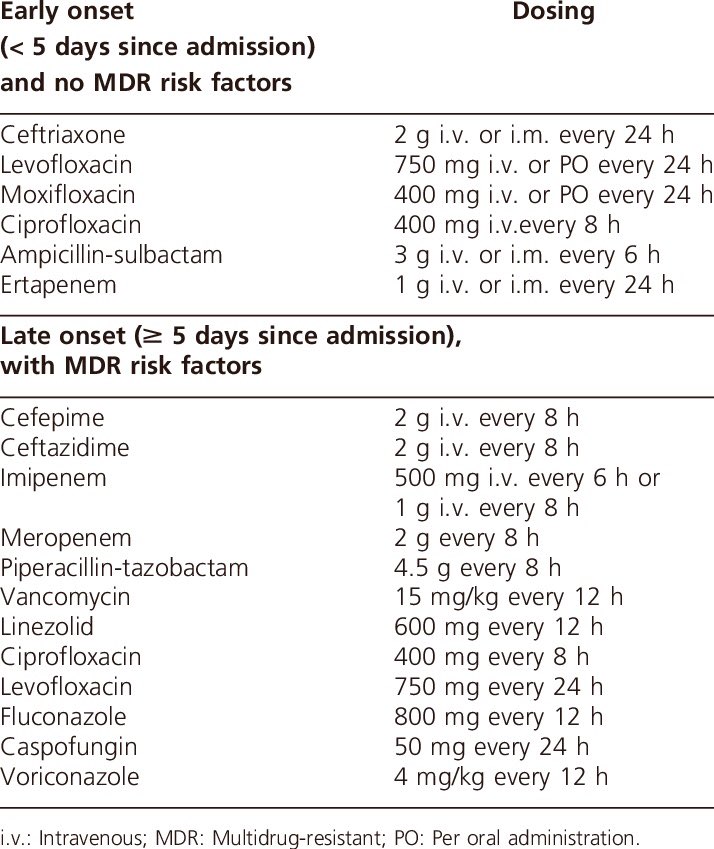
#ثريد اليوم عن pneumonia للمختصين في المجال الصحي انشاء الله يعجبكم ❤️
Signs and symptoms
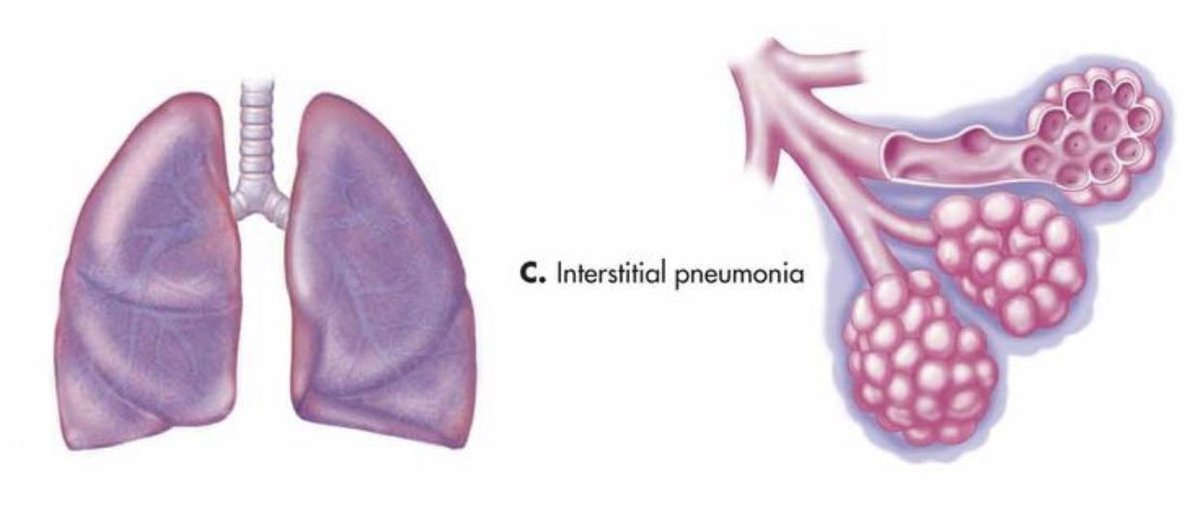
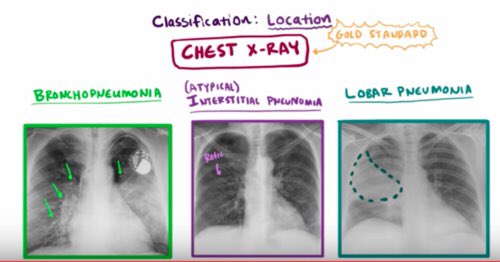
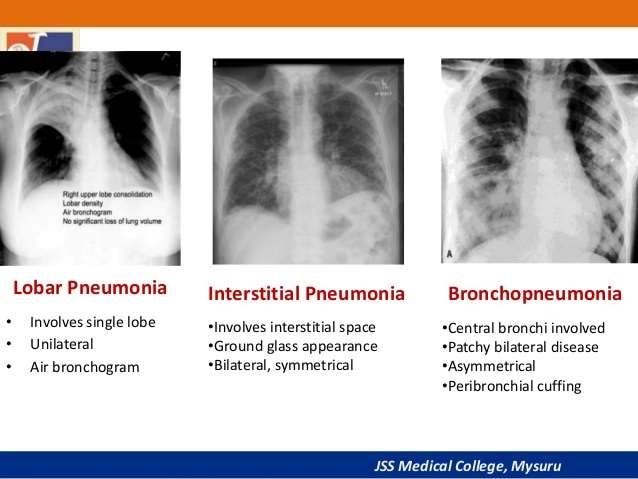
1-Typical pneumonia is characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms caused by lobar infiltration.
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Pyrexia (fever)
Reproductive cough
Fatigue
SOB
1-Typical pneumonia is characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms caused by lobar infiltration.
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Pyrexia (fever)
Reproductive cough
Fatigue
SOB
2-Atypical pneumonia:
typically has an indolent course (slow onset) and commonly manifests with extra pulmonary symptoms.
-Nonproductive, dry cough
-Dyspnea
-Common extrapulmonary features include fatigue, headaches, sore throat, myalgias, and malaise.
typically has an indolent course (slow onset) and commonly manifests with extra pulmonary symptoms.
-Nonproductive, dry cough
-Dyspnea
-Common extrapulmonary features include fatigue, headaches, sore throat, myalgias, and malaise.
بكذا انتهى الثريد حاولت ابسطه بقدر الامكان، بما انه موضوع كبير ويحتاج تعمق راح اتركلهم رابط لمقال جدا رهيب ومرتب وان شاء الله اكون وفقت في هذا الثريد ❤️
amboss.com
amboss.com
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...