#ثريد اليوم عن Bradycardia للمهتمين في المجال الصحي 💉
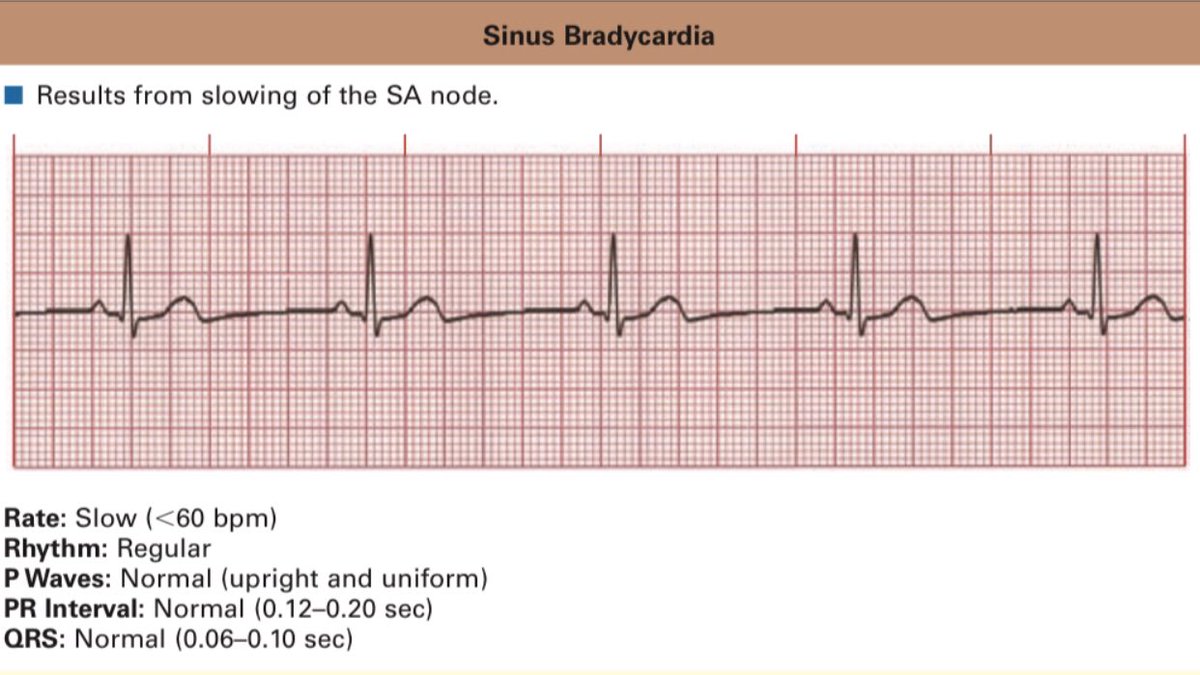
Bradycardia is a condition typically defined wherein an individual has a resting heart rate of under 60 beats per minute (BPM) in adults, although some studies use a heart rate of less than 50 BPM.
Bradycardia typically does not cause symptoms until the rate drops below 50 BPM
Bradycardia typically does not cause symptoms until the rate drops below 50 BPM
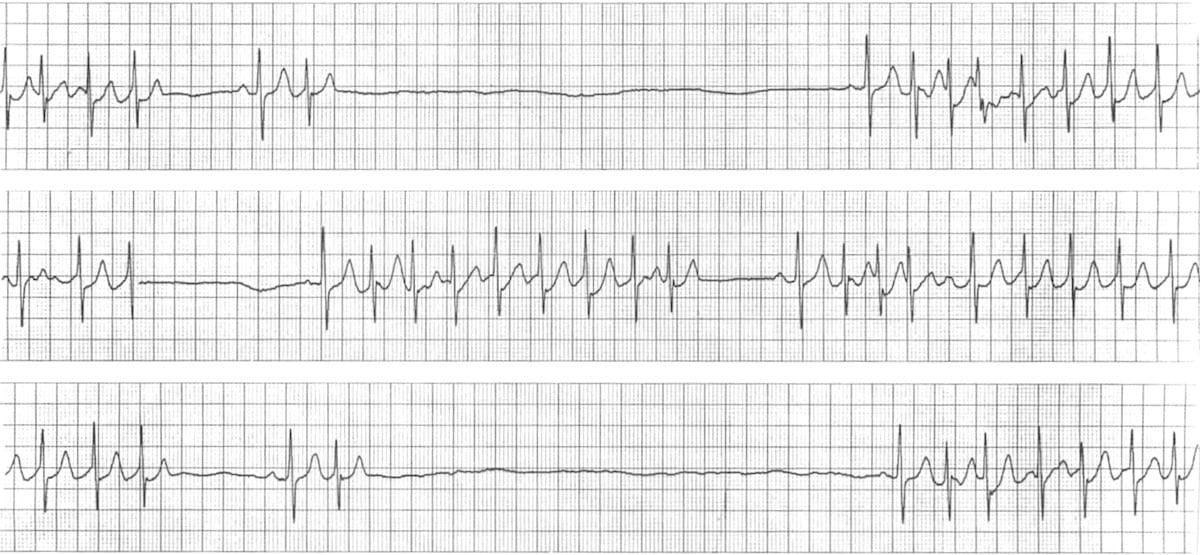
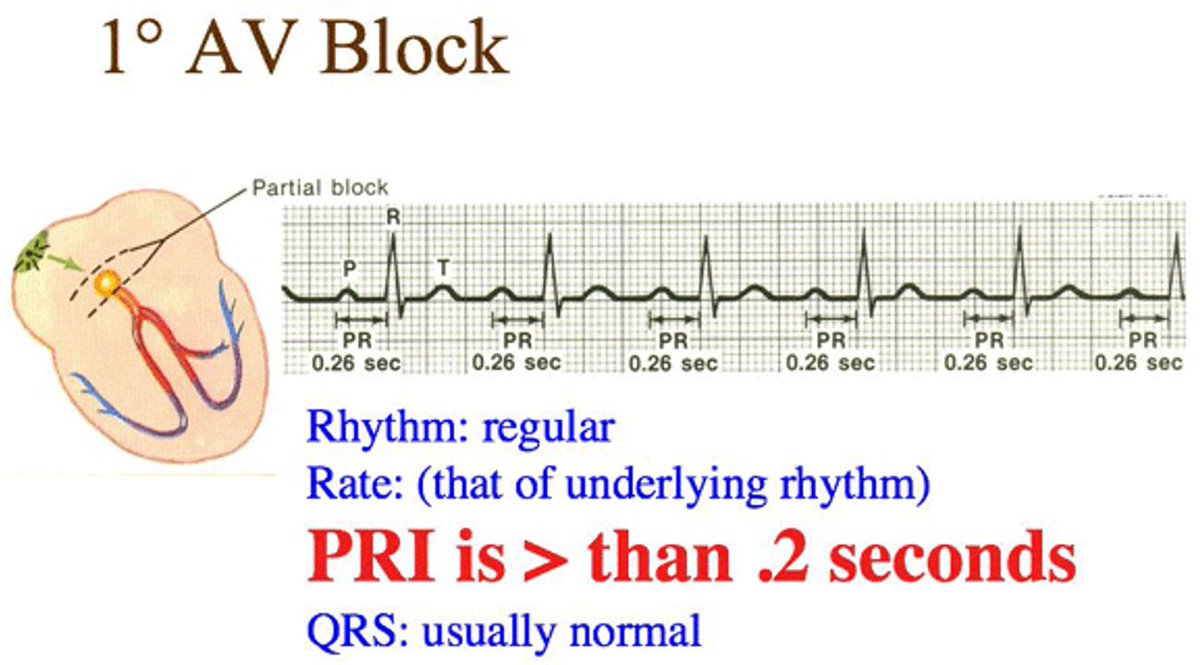
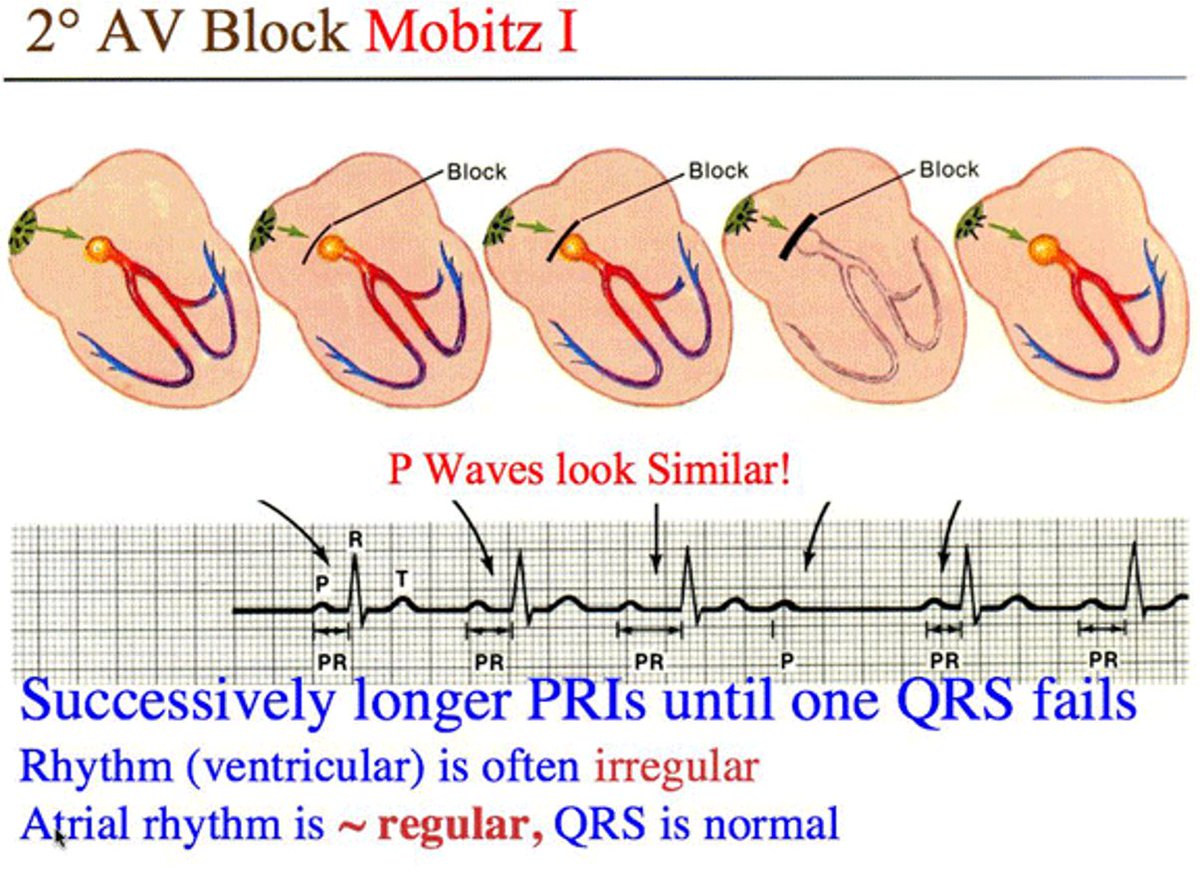
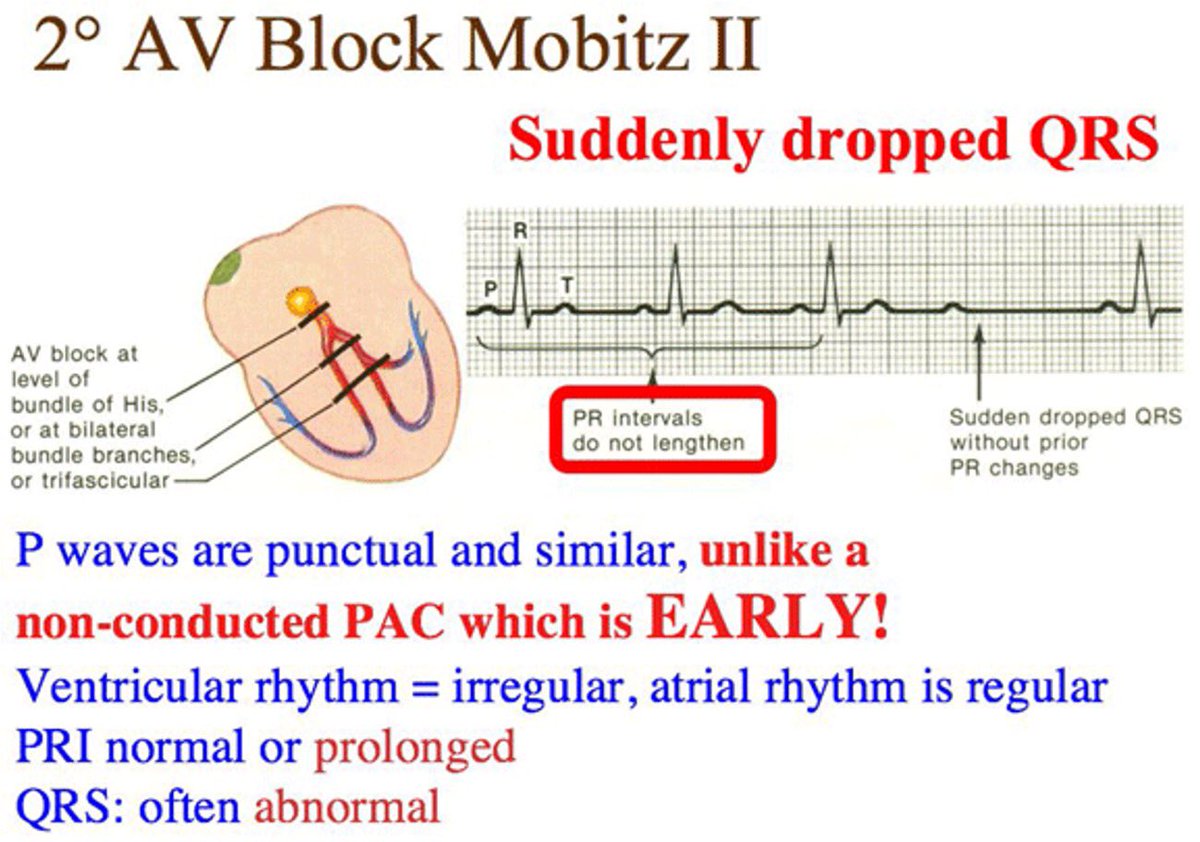
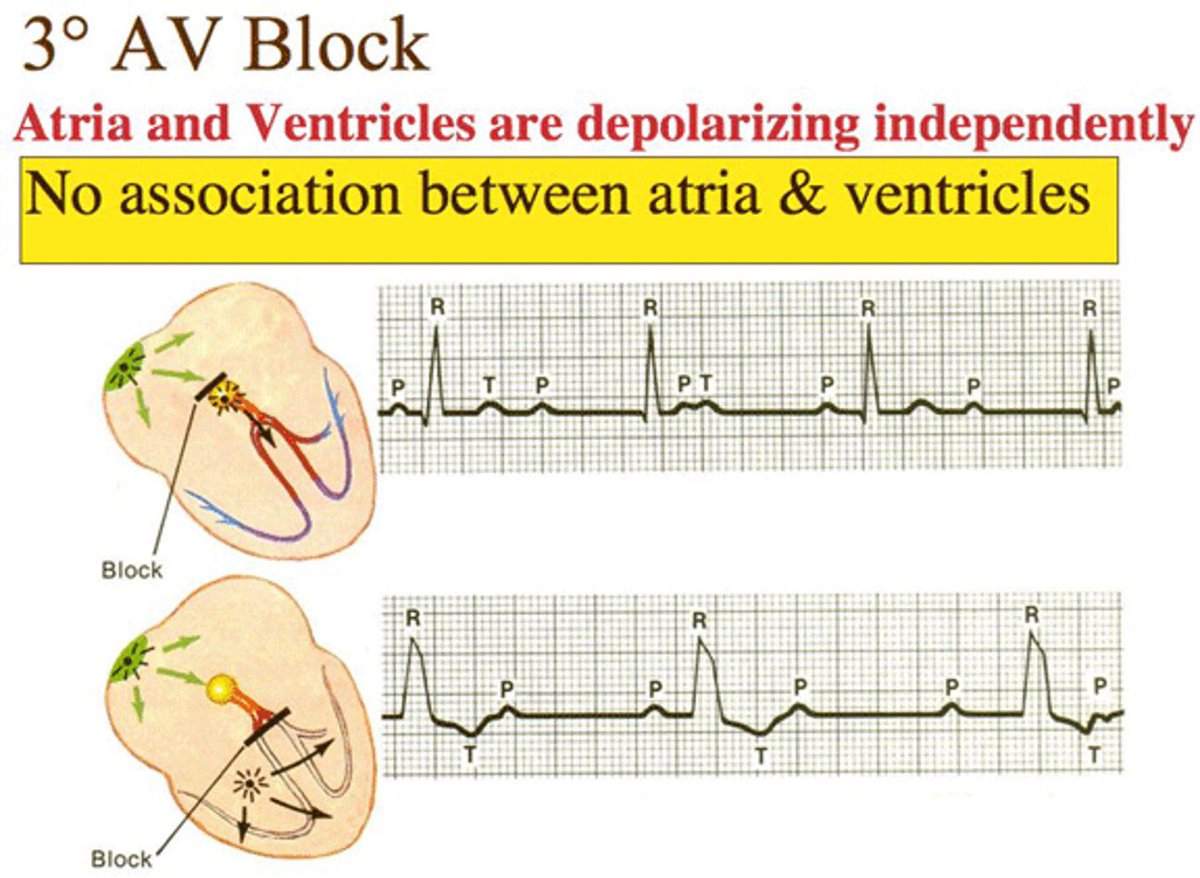
3- Heart block (AV) block is a complete or partial interruption of the electrical impulses on their way to the ventricles and results in a slow, unreliable heartbeat.Heart block may be present at birth, heart disease or due to age-related and tear on the heart's electrical system
Note 📝 Usually AV block is benign, but if associated with an acute MI, it may lead to further AV defects.
Note 📝 Mobitz I type II AV block may be caused by medication such as beta blockers, digoxin, and calcium channel blockers. Ischemia involving the right coronary artery is another cause.
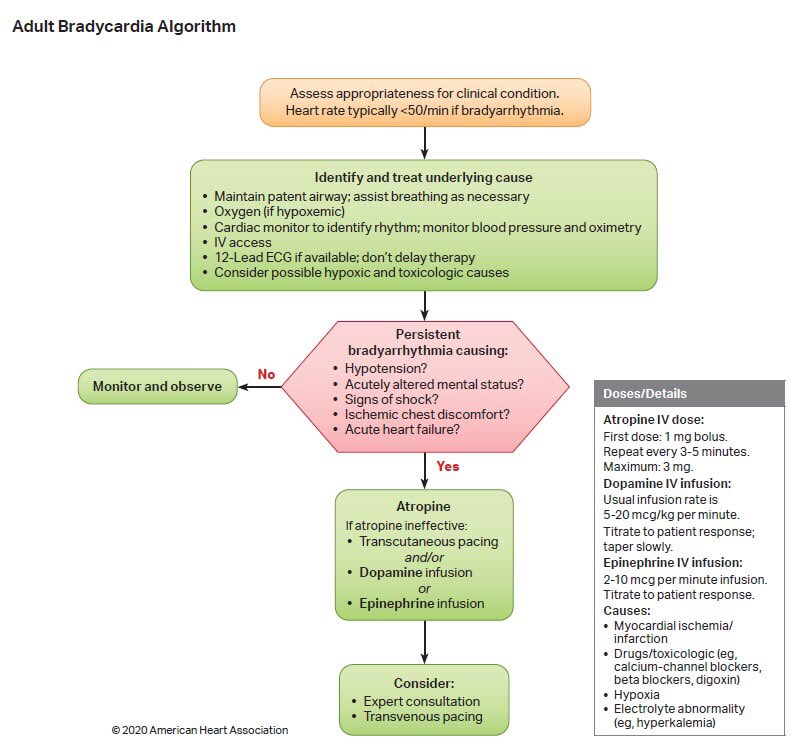
How to deal with bradycardia
1- Pulse rate 60 bpm?
2- persistent causes (hypotension, alter mental status, shock, chest pain, HF).
3- if yes Measure vital signs, including oxygen saturation.
4- Supply oxygen, begin cardiac monitoring, and start IV.
1- Pulse rate 60 bpm?
2- persistent causes (hypotension, alter mental status, shock, chest pain, HF).
3- if yes Measure vital signs, including oxygen saturation.
4- Supply oxygen, begin cardiac monitoring, and start IV.
5- administer atropine 0.5–1.0 mg IVP every 3–5 min, max. 0.03–0.04 mg/kg.
6- If patient remains symptomatic or has 2nd-degree (Mobitz type II) or 3rd-degree AV block, sedate patient and begin transcutaneous pacing, if available.
6- If patient remains symptomatic or has 2nd-degree (Mobitz type II) or 3rd-degree AV block, sedate patient and begin transcutaneous pacing, if available.
7- If no response, consider dopamine with continuous infusions (titrate to patient response) of 5–20 g/kg/min. Mix 400 mg/250 mL in normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution, or D5W.
8- If patient is still hypotensive with severe bradycardia, consider epinephrine infusion, 2–10 g/min IV (add 1 mg of 1:1000 to 500 mL normal saline and infuse at 1–5 mL/min).
9- If still no response, consider isoproterenol, IV infusion: mix 1 mg in 250 mL normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution, or D5W with rate of 2–10 g/min, titrate to patient response.
Note 📝 If patient is symptomatic, do not delay transcutaneous pacing while waiting for atropine to take effect or for IV access.
Use atropine with caution in a suspected acute MI; atropine may induce rate-related ischemia.
Use atropine with caution in a suspected acute MI; atropine may induce rate-related ischemia.
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...