Types of tachycardia
A-Narrow QRS tachycardia:
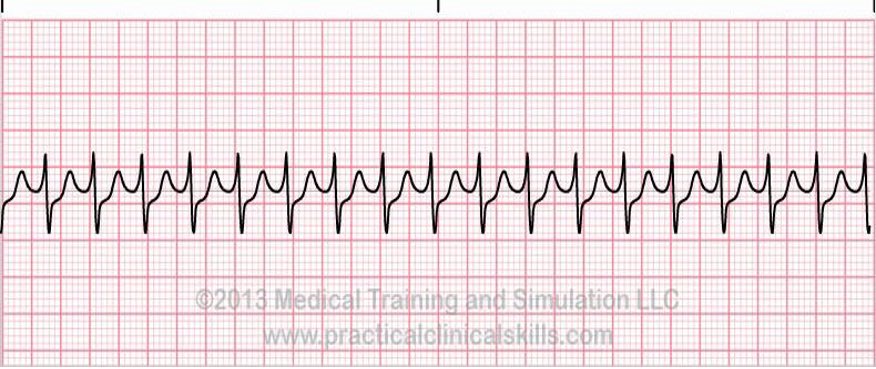
1. Sinus tachycardia
2. Supraventricular tachycardia (all the 3 below is types of SVT)+ proximal SVT.
3. Atrial flutter
4. Atrial fibrillation (irregular)
5. AV nodal reentry
A-Narrow QRS tachycardia:
1. Sinus tachycardia
2. Supraventricular tachycardia (all the 3 below is types of SVT)+ proximal SVT.
3. Atrial flutter
4. Atrial fibrillation (irregular)
5. AV nodal reentry
Wide QRS COMPLEX tachycardia:
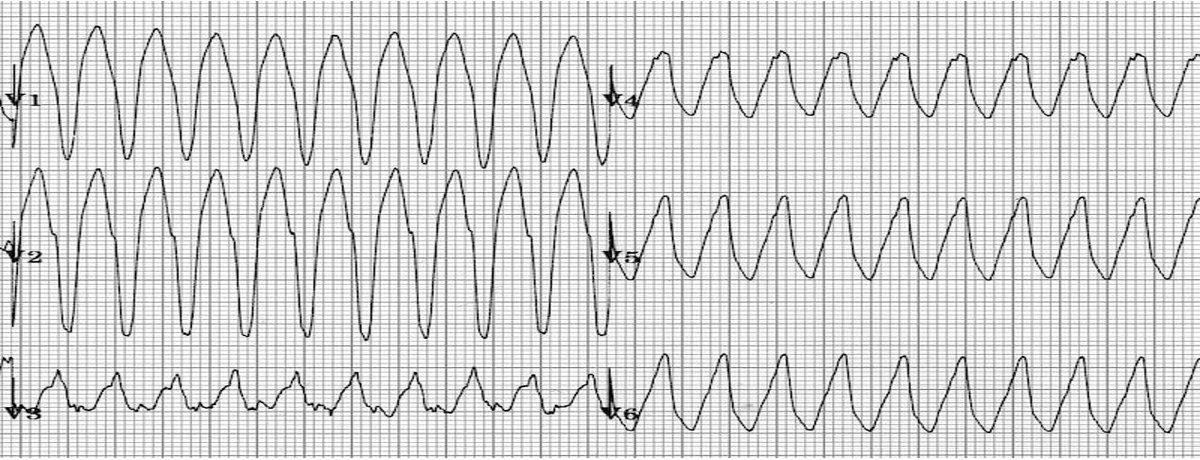
1. Monomorphic VT (regular)
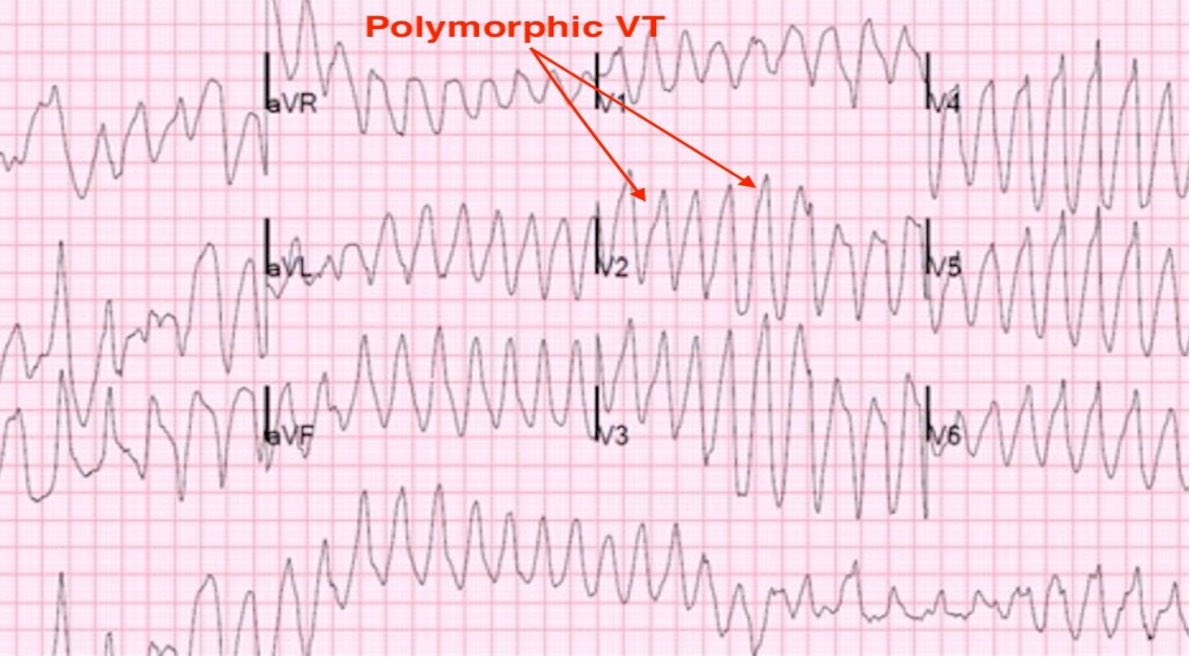
2. Polymorphic VT (irregular)
3. SVT with aberrancy
1. Monomorphic VT (regular)
2. Polymorphic VT (irregular)
3. SVT with aberrancy
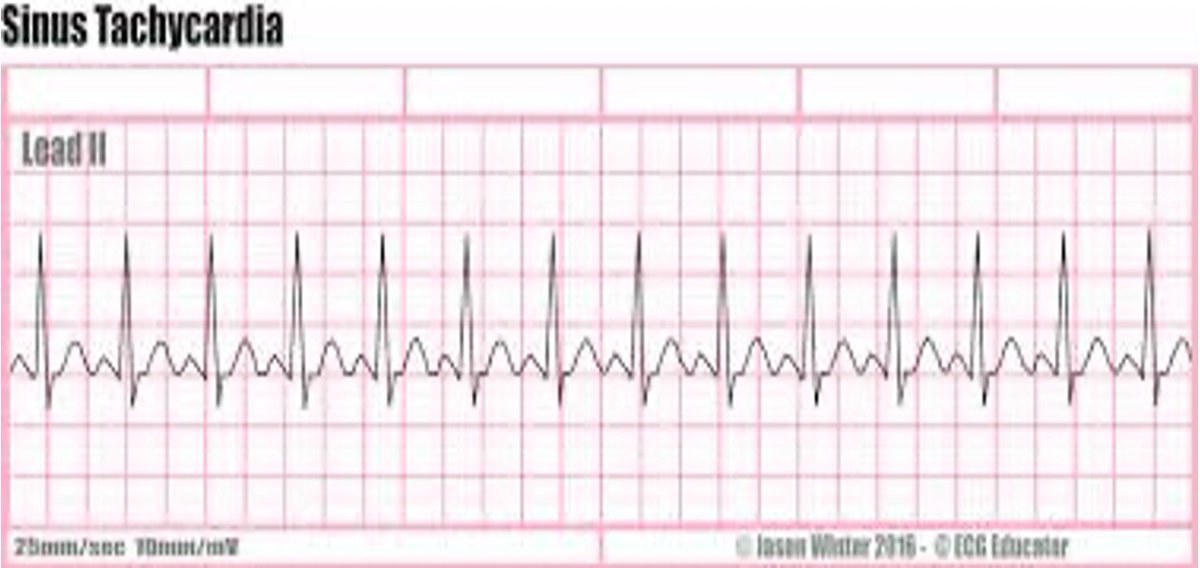
ECG findings in sinus tachycardia:
• P waves: Normal and upright
• QRS complex: Less than 0.12 second • Rate: more than 100 beats/minute
• Rhythm: Regular
• P-R interval: 0.12 to 0.20 second
Management: Treat causes
• P waves: Normal and upright
• QRS complex: Less than 0.12 second • Rate: more than 100 beats/minute
• Rhythm: Regular
• P-R interval: 0.12 to 0.20 second
Management: Treat causes
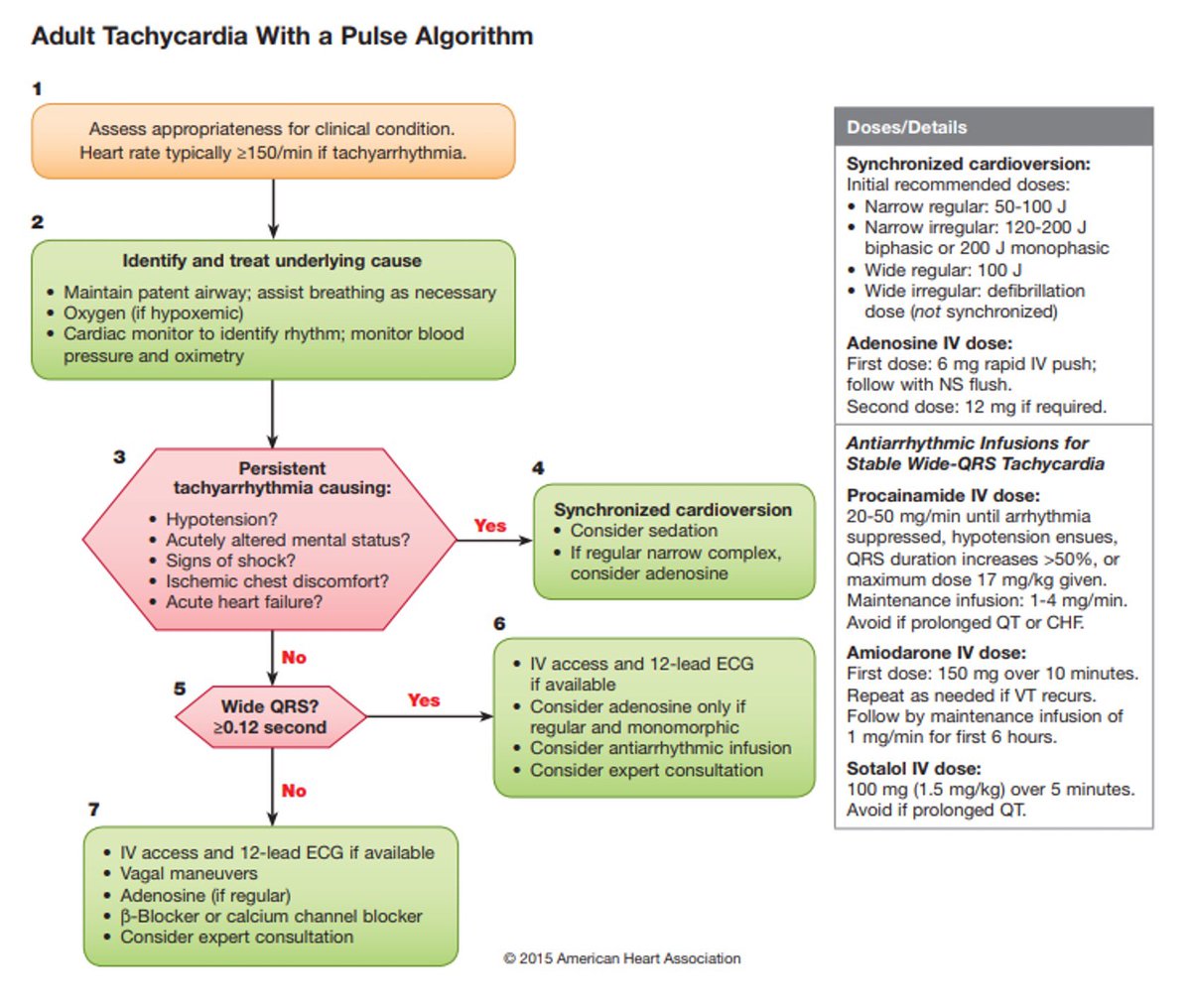
management:
If the patient is stable:
Vagal Maneuvers , Valsalva maneuver
Medication:
Adenosine: 6 mg rapid IV, if no conversion, give 12 mg IV (second dose) Diltiazem or verapamil (calcium channel blocker).
Stalol beta blocker 100mg or 1.5/kg over 5 min avoid it if prolonged QT
If the patient is stable:
Vagal Maneuvers , Valsalva maneuver
Medication:
Adenosine: 6 mg rapid IV, if no conversion, give 12 mg IV (second dose) Diltiazem or verapamil (calcium channel blocker).
Stalol beta blocker 100mg or 1.5/kg over 5 min avoid it if prolonged QT
If unstoppable:
Cardioversion 50-100J, consider adenosine and consultation.
Cardioversion 50-100J, consider adenosine and consultation.
Management:
If stable pt:
-Beta blockers (stalol 100mg or 1.5/kg over 5 min avoid it if prolonged QT). -Calcium channel blocking agents used in caution with:
Congestive heart failure, Asthma, COPD
-Digoxin
Synchronized shock of 50 J (initial attempt) to 100 J.
If stable pt:
-Beta blockers (stalol 100mg or 1.5/kg over 5 min avoid it if prolonged QT). -Calcium channel blocking agents used in caution with:
Congestive heart failure, Asthma, COPD
-Digoxin
Synchronized shock of 50 J (initial attempt) to 100 J.
Management:
If stable pt:
Beta blockers (stalol 10mg or 1,5/kg over 5 min avoid it if prolonged QT) -Calcium channel blocking agents used in caution with:
Congestive heart failure, Asthma, COPD
-Digoxin
If unstable pt:
Synchronized shock of 100 to 120 J biphasic (200 J monophasic
If stable pt:
Beta blockers (stalol 10mg or 1,5/kg over 5 min avoid it if prolonged QT) -Calcium channel blocking agents used in caution with:
Congestive heart failure, Asthma, COPD
-Digoxin
If unstable pt:
Synchronized shock of 100 to 120 J biphasic (200 J monophasic
Management:
If stable pt:
Amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 minutes
Procainamide 20-50 mg (alternative drug) avoid it if prolong QT, CHF
If unstable pt:
synchronized cardioversion Begin with 100 J, If no response, dose should be increased at 200 J, 300 J, and 360 J monophasic
If stable pt:
Amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 minutes
Procainamide 20-50 mg (alternative drug) avoid it if prolong QT, CHF
If unstable pt:
synchronized cardioversion Begin with 100 J, If no response, dose should be increased at 200 J, 300 J, and 360 J monophasic
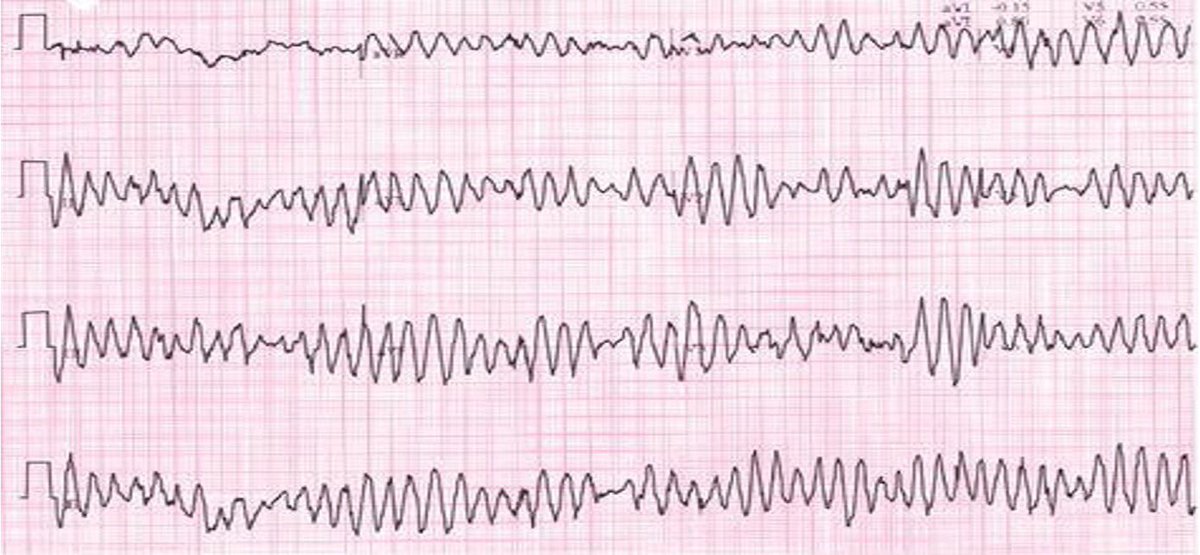
Management:
Treated as ventricular fibrillation High-energy unsynchronized shocks
Treated as ventricular fibrillation High-energy unsynchronized shocks
Management:
Medications that prolong Q-T interval should be discontinued. Electrolyte imbalances should be corrected
IV magnesium sulfate should be given
Medications that prolong Q-T interval should be discontinued. Electrolyte imbalances should be corrected
IV magnesium sulfate should be given
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...