o Large family of secretory proteins (cytokines)
o Prevent virus replication inside the cells
o Prevent virus replication inside the cells
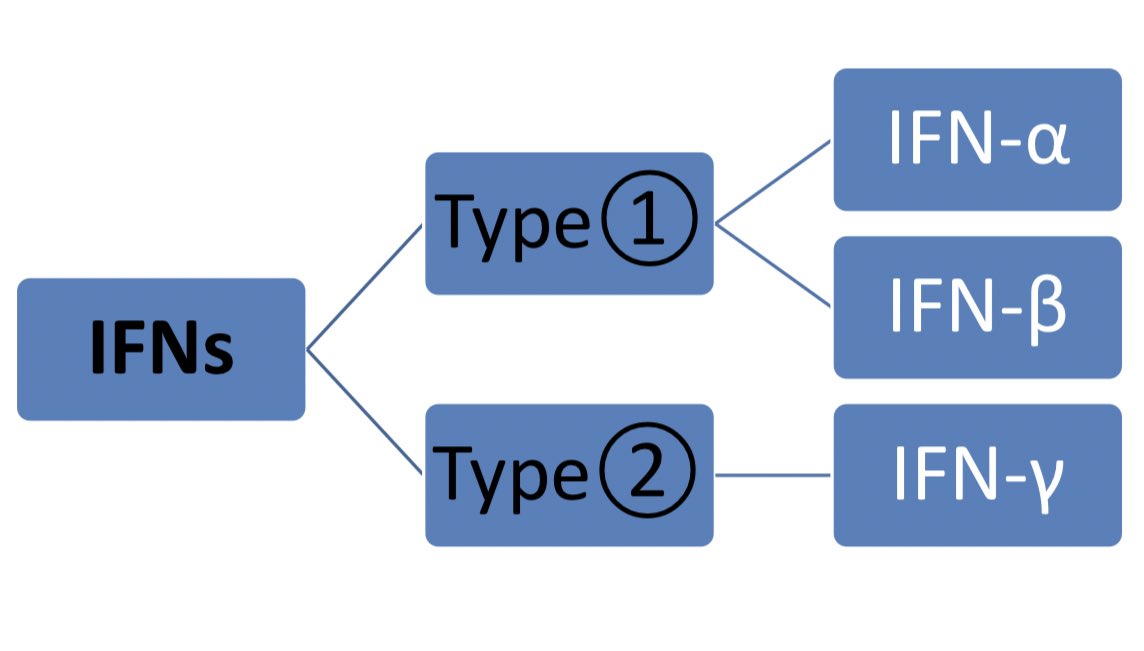
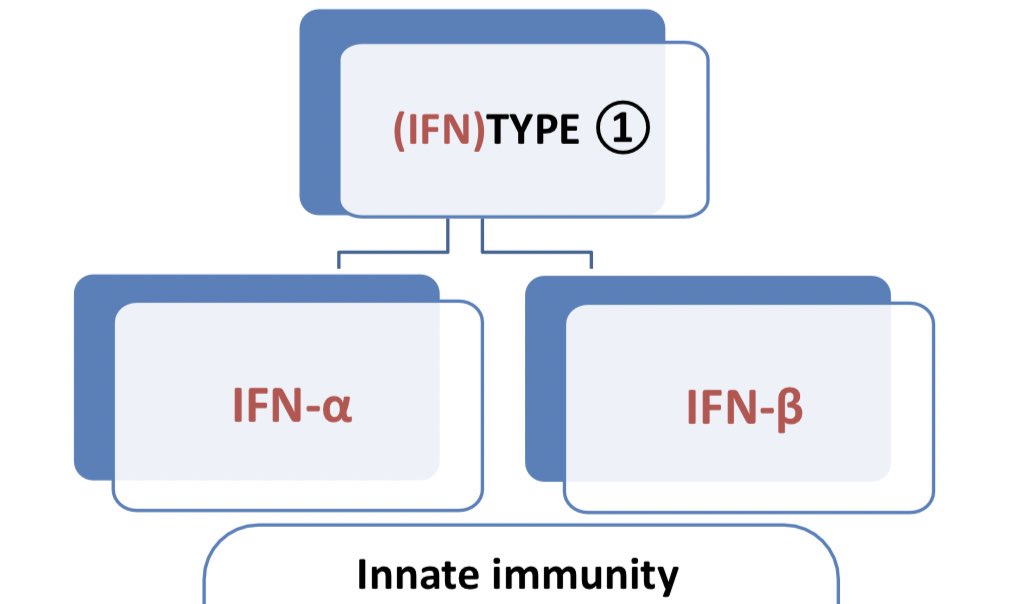
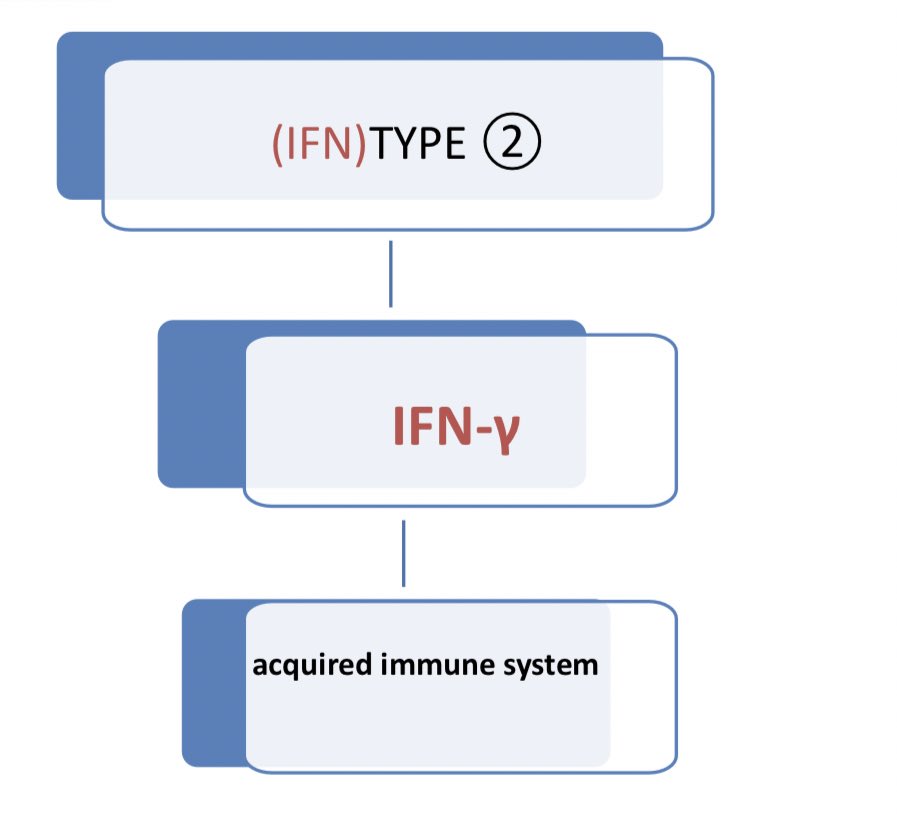
•Both α and β interferons identical in funcation and structure, produced in response to virus, where as Υ interferon produced from antigen activated T lymphocytes.
• Chemically interferons are glycoprotein in nature having molecular weight 20,000 to 40,000
• Chemically interferons are glycoprotein in nature having molecular weight 20,000 to 40,000
*General characteristics of interferons are:📝🔍
•They are stable over a wide range of pH ( 2 to 10).
•They do not have any direct action on viruses.
•Their activities are not virus specific. Interferons induced by one virus is effective against many other viruses
•They are stable over a wide range of pH ( 2 to 10).
•They do not have any direct action on viruses.
•Their activities are not virus specific. Interferons induced by one virus is effective against many other viruses
•Synthesis of interferons begins within one hour of induction and takes about 12 hours to reach its maximum activity.
•t is nontoxic, nonantigenic, diffuses freely in the body and has a wide spectrum of antiviral activity.
•t is nontoxic, nonantigenic, diffuses freely in the body and has a wide spectrum of antiviral activity.
*Producing (IFN)TYPE 1📝🔬
•IFN-α are secrated by viraaly infected leukocytes
•IFN-α are secrated by viraaly infected leukocytes
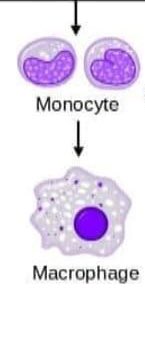
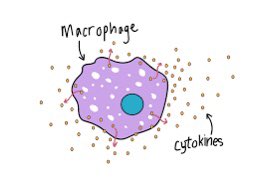
e.x: Monocytes : are a type of leukocyte, or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte and can differentiate into macrophages
play more than one role in protecting against invasion and tissue injury.
•Stimulate the immune responses associated with antibody-mediated immunity (AMI) (Macropha interact with T-helper cells and activate them ),then T-helper cells activate B-cell to produce antibody
•Stimulate the immune responses associated with antibody-mediated immunity (AMI) (Macropha interact with T-helper cells and activate them ),then T-helper cells activate B-cell to produce antibody
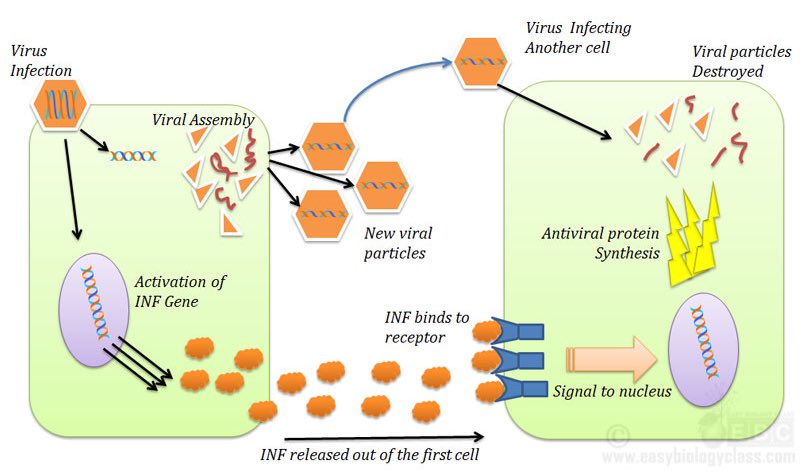
Interferon is secreted by cells in response to stimulation by a virus, but it does not directly inhibit the virus's multiplication. Rather, it stimulates the infected cells and those nearby to produce proteins that prevent the virus from replicating within them.
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...