#respiratory
📍Management of COPD Exacerbation:
•Oxygen + ABGs
•Bronchodilators: Nebulised salbutamol 5mg and ipratropium bromide 500 microgram immediately and then 4-6 hourly
•Steroids: Prednisolone 40mg oral od
•antibiotics if indicted (amoxicillin oral)
📍Management of COPD Exacerbation:
•Oxygen + ABGs
•Bronchodilators: Nebulised salbutamol 5mg and ipratropium bromide 500 microgram immediately and then 4-6 hourly
•Steroids: Prednisolone 40mg oral od
•antibiotics if indicted (amoxicillin oral)
?Management of Asthma Exacerbation:
•Oxygen + ABGs
•asses severity of acute asthma
•Bronchodilators: Nebulised salbutamol 5mg, repeated every 10 minutes if necessary. Consider nebulised ipratropium in severe or life-threatening episodes
•Steroids: Prednisolone 40mg oral
•Oxygen + ABGs
•asses severity of acute asthma
•Bronchodilators: Nebulised salbutamol 5mg, repeated every 10 minutes if necessary. Consider nebulised ipratropium in severe or life-threatening episodes
•Steroids: Prednisolone 40mg oral
Management of Hyperkalaemia ?? #med15
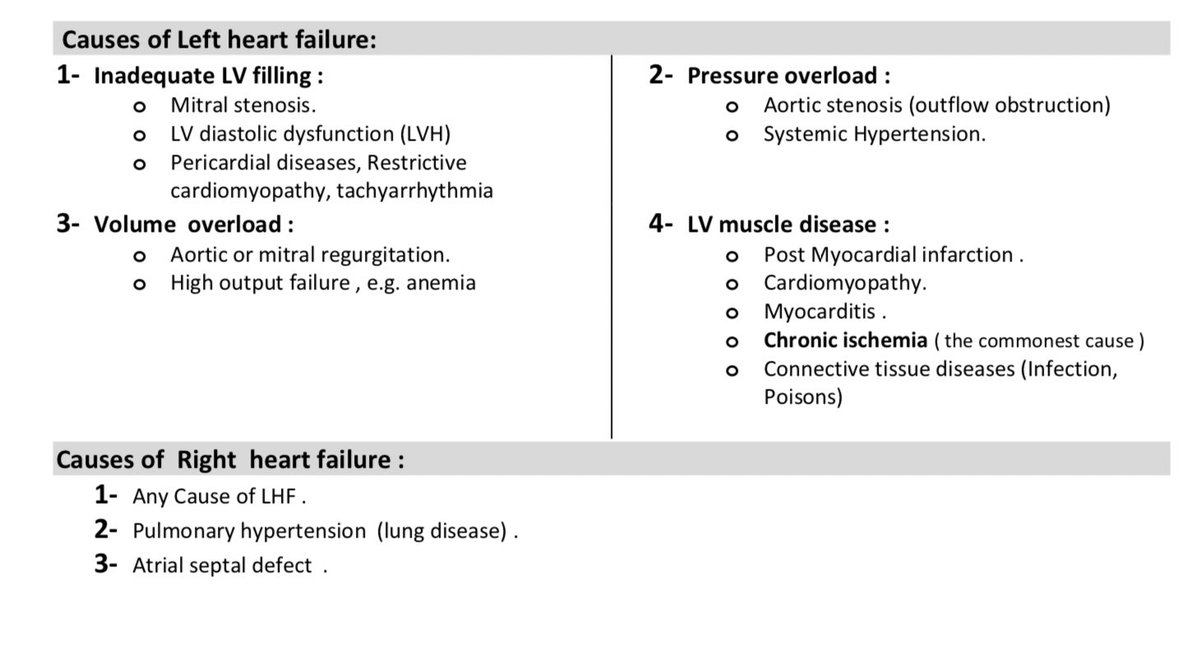
?Causes of Heart Failure ? #med15
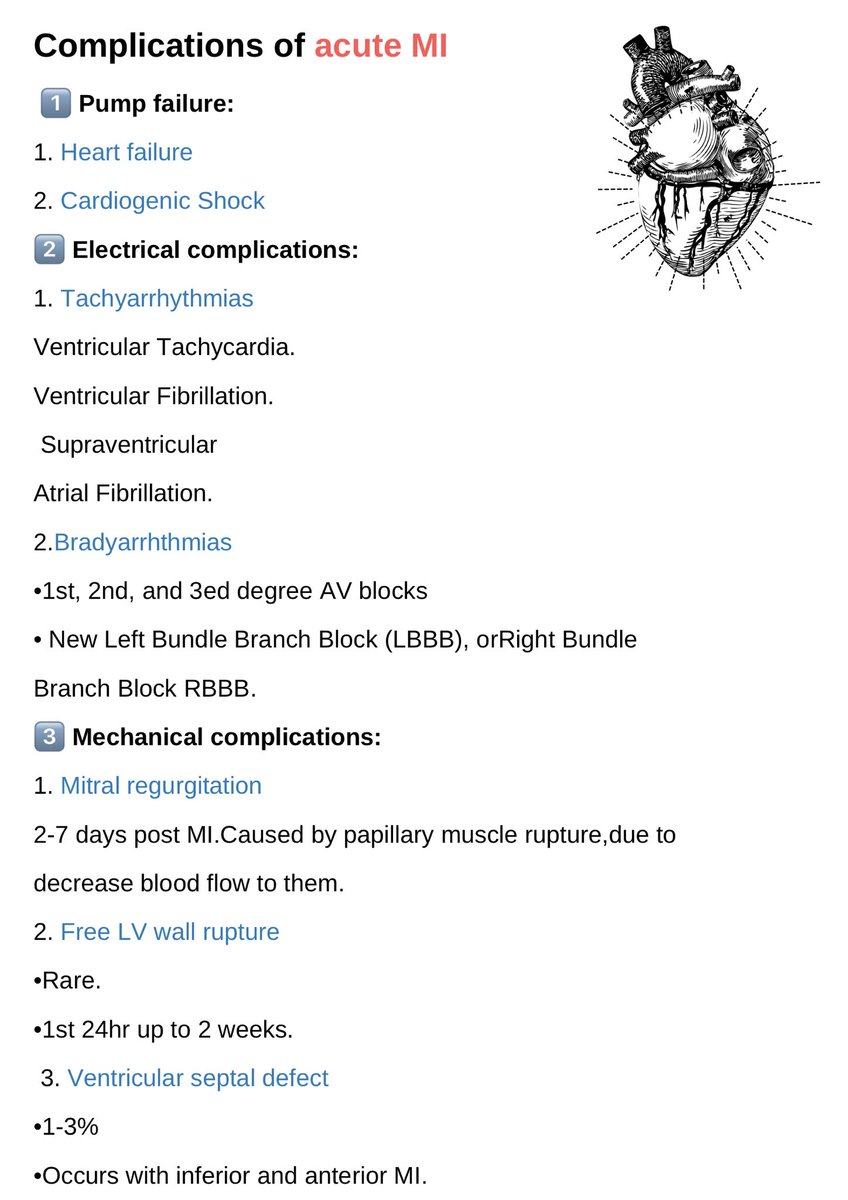
?List six mechanical complications that may follow an AMI:
✅Left ventricular aneurysm
✅rupture, papillary muscle rupture
✅dysfunction, thromboembolism
✅reinfarction or extension
✅pericardial effusion or tamponade
✅heart failure
✅Left ventricular aneurysm
✅rupture, papillary muscle rupture
✅dysfunction, thromboembolism
✅reinfarction or extension
✅pericardial effusion or tamponade
✅heart failure
?What connective tissue and arthritic syndromes are associated with Aortic regurgitation ?
✅Marfan's syndrome
✅Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
✅Reiter's
✅rheumatoid arthritis
✅systemic lupus erythematosus
✅Takayasu's aortitis
✅Marfan's syndrome
✅Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
✅Reiter's
✅rheumatoid arthritis
✅systemic lupus erythematosus
✅Takayasu's aortitis
?which of the patient groups should receive endocarditis prophylaxis?
✅Patients with prosthetic heart valves
✅Patients with a history of IE
✅Patients with unrepaired congenital heart disease
✅Patients with repaired congenital disease but
residual defects
✅Patients with prosthetic heart valves
✅Patients with a history of IE
✅Patients with unrepaired congenital heart disease
✅Patients with repaired congenital disease but
residual defects
#cardiology
?What are some potential side effects of ACEIs??
✅ Hypotension,
✅ renal failure (in patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis) ✅hyperkalemia
✅allergic reactions (the most serious of which is angioedema) ✅cough
?What are some potential side effects of ACEIs??
✅ Hypotension,
✅ renal failure (in patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis) ✅hyperkalemia
✅allergic reactions (the most serious of which is angioedema) ✅cough
#GIT
?Causes of Hepatomegaly
•Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
•Metastatic liver disease
•Cirrhosis
•Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
•Hepatitis
•Leukaemia
•Lymphoma
?Causes of Hepatomegaly
•Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
•Metastatic liver disease
•Cirrhosis
•Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
•Hepatitis
•Leukaemia
•Lymphoma
?Causes of Splenomegaly
•MASSIVE: Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia, Myelofibrosis, Kala-azar
•MODERATE: Lymphoma, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia, Malaria
•MILD: Epstein-Barr virus, Hepatitis, Portal Hypertension, Rheumatoid Arthritis (Felty’s Syndrome)
•MASSIVE: Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia, Myelofibrosis, Kala-azar
•MODERATE: Lymphoma, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia, Malaria
•MILD: Epstein-Barr virus, Hepatitis, Portal Hypertension, Rheumatoid Arthritis (Felty’s Syndrome)
how to differentiate btw spleen and kidney
Spleen❇️
- notch present
-Dull to percussion?
-Can’t get between the ribs and spleen
-moves down on inspiration ?
Kidney❇️
-No notch present
-Resonant to percussion ?
-can get fingers over the kidney?
-doesn’t move with breathing.
Spleen❇️
- notch present
-Dull to percussion?
-Can’t get between the ribs and spleen
-moves down on inspiration ?
Kidney❇️
-No notch present
-Resonant to percussion ?
-can get fingers over the kidney?
-doesn’t move with breathing.
?What are the causes of a distended abdomen?
✅Fat ✅fluid ✅Faeces ✅Flatus ✅Fetus
?What do you understand by the term ascites?
It’s the pathological accumulation of Fluid in the peritoneal cavity
✅Fat ✅fluid ✅Faeces ✅Flatus ✅Fetus
?What do you understand by the term ascites?
It’s the pathological accumulation of Fluid in the peritoneal cavity
?What are the common causes of ascites?
?Portal hypertension with cirrhosis.
?Abdominal malignancy.
? congestive cardiac failure.
?What Investigation would you do to determine the underlying cause of ascites?
?Paracentesis
?US
?Peritoneal biopsy or laparoscopy
?Portal hypertension with cirrhosis.
?Abdominal malignancy.
? congestive cardiac failure.
?What Investigation would you do to determine the underlying cause of ascites?
?Paracentesis
?US
?Peritoneal biopsy or laparoscopy
?What is the difference btw an exudate and a transudate?
?An exudate has a protein content of >25 g/l.
?An exudate has a protein content of >25 g/l.
?Causes of liver Cirrhosis :
1. Chronic viral hepatitis.
2. Metabolic: hemochromatosis, Wilson dis, alfa-1-
antitrypsin, NASH.
3. Prolonged cholestasis (primary biliary cirrhosis, primary
sclerosing cholangitis).
4. Autoimmune diseases (autoimmune hepatitis).
5. Drugs and toxin
1. Chronic viral hepatitis.
2. Metabolic: hemochromatosis, Wilson dis, alfa-1-
antitrypsin, NASH.
3. Prolonged cholestasis (primary biliary cirrhosis, primary
sclerosing cholangitis).
4. Autoimmune diseases (autoimmune hepatitis).
5. Drugs and toxin
?Complications of Portal Hypertension❓
1️⃣ Varices :
•Esophagus.
•Gastric.
•Colorectal.
•Portal hypertensive gastropathy.
2️⃣ Ascites
Causes of Ascites :
1. Liver disease: cirrhosis.
2. Right sided heart failure.
3. Kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome).
4.Low albumin
1️⃣ Varices :
•Esophagus.
•Gastric.
•Colorectal.
•Portal hypertensive gastropathy.
2️⃣ Ascites
Causes of Ascites :
1. Liver disease: cirrhosis.
2. Right sided heart failure.
3. Kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome).
4.Low albumin
?Diagnosis of Ascites:
•Physical examination.
• Ultrasound.
•Ascitic tap
? WBC (>250 PMN: SBP).
? RBC.
? SAAG(serum albumin to ascitic fluid albumin gradient)
>11 mg/dl : portal hypertension.
<11 mg/dl : Other.
•Physical examination.
• Ultrasound.
•Ascitic tap
? WBC (>250 PMN: SBP).
? RBC.
? SAAG(serum albumin to ascitic fluid albumin gradient)
>11 mg/dl : portal hypertension.
<11 mg/dl : Other.
?Treatment-General of Ascites
•Treat the underlying disease.
• Salt restriction
• Diuretics
• Loop diuretic
• Aldosterone inhibitor (Spironolactone).
?Treatment-Resistant :
• Recurrent tapping.
•Peritoneal-venous shunt.
• TIPS.
•Liver transplantation.
•Treat the underlying disease.
• Salt restriction
• Diuretics
• Loop diuretic
• Aldosterone inhibitor (Spironolactone).
?Treatment-Resistant :
• Recurrent tapping.
•Peritoneal-venous shunt.
• TIPS.
•Liver transplantation.
?Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis :
• Infection of ascitic fluid.
• Usually gram negative (E.Coli).
• Presentation variable.
• Mortality is high.
• Dx : ascitic tap = PMN>250
• Treatment : third generation cephalosporin IV.
• Infection of ascitic fluid.
• Usually gram negative (E.Coli).
• Presentation variable.
• Mortality is high.
• Dx : ascitic tap = PMN>250
• Treatment : third generation cephalosporin IV.
? Hepatic encephalopathy?
Risk Factors:
•Deterioration of liver function
•Infections
•Gastrointestinal bleeding
•Constipation
•Portal vein thrombosis
•Renal failure
•Excessive protein consumption
? Diagnostics
•Elevated blood ammonia levels
Risk Factors:
•Deterioration of liver function
•Infections
•Gastrointestinal bleeding
•Constipation
•Portal vein thrombosis
•Renal failure
•Excessive protein consumption
? Diagnostics
•Elevated blood ammonia levels
?Treatment of Hepatic encephalopathy:
• Identify and treat precipitation factor.
•Treat underlying liver disease.
• Normal protein diet (not low).
•Antibiotics (Neomycin, metronidazole).
• Lactolose.
• Transplantation.
• Identify and treat precipitation factor.
•Treat underlying liver disease.
• Normal protein diet (not low).
•Antibiotics (Neomycin, metronidazole).
• Lactolose.
• Transplantation.
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...